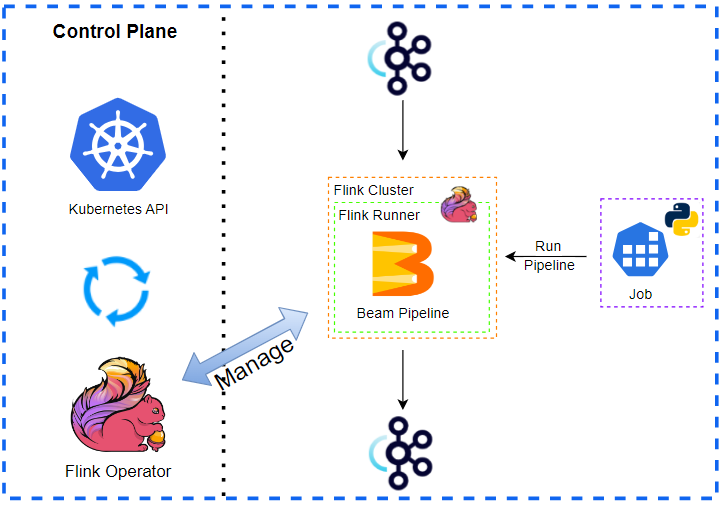
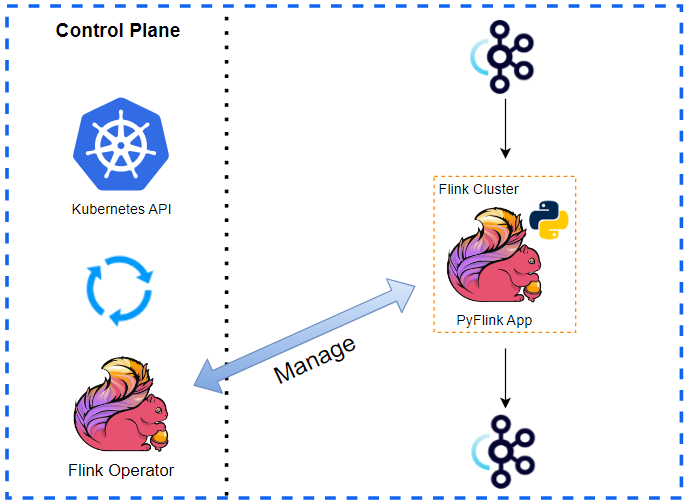
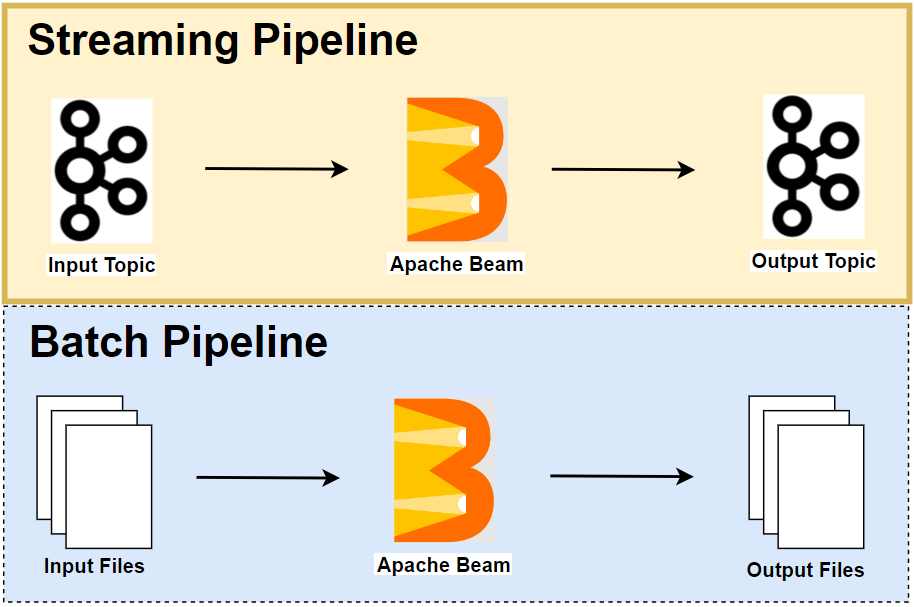
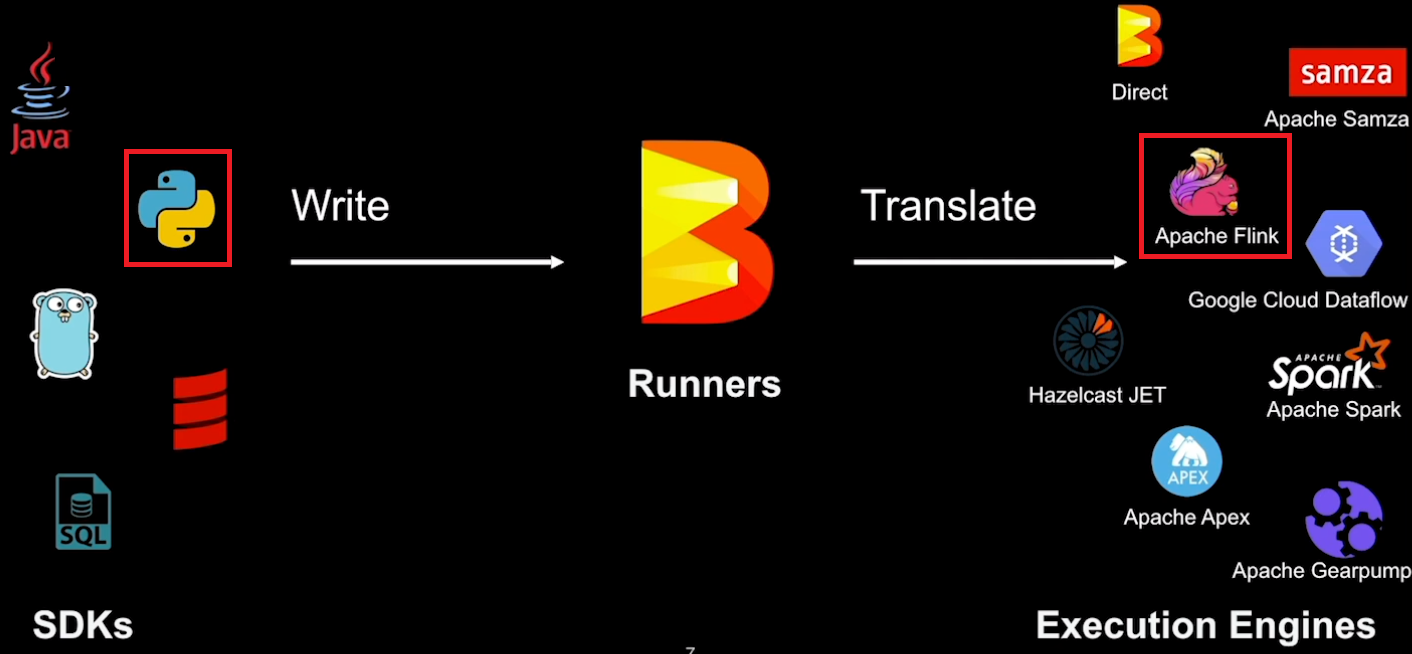
Beam pipelines are portable between batch and streaming semantics but not every Runner is equally capable. The Apache Flink Runner supports Python, and it has good features that allow us to develop streaming pipelines effectively. We first discuss the portability layer of Apache Beam as it helps understand (1) how a pipeline developed by the Python SDK can be executed in the Flink Runner that only understands Java JAR and (2) how multiple SDKs can be used in a single pipeline. Then we move on to how to manage local Flink and Kafka clusters using bash scripts. Finally, we end up illustrating a simple streaming pipeline, which reads and writes website visit logs from and to Kafka topics.