In this lab, we will create a Pyflink application that reads records from S3 and sends them into a Kafka topic. A custom pipeline Jar file will be created as the Kafka cluster is authenticated by IAM, and it will be demonstrated how to execute the app in a Flink cluster deployed on Docker as well as locally as a typical Python app. We can assume the S3 data is static metadata that needs to be joined into another stream, and this exercise can be useful for data enrichment.
- Introduction
- Lab 1 Produce data to Kafka using Lambda
- Lab 2 Write data to Kafka from S3 using Flink (this post)
- Lab 3 Transform and write data to S3 from Kafka using Flink
- Lab 4 Clean, Aggregate, and Enrich Events with Flink
- Lab 5 Write data to DynamoDB using Kafka Connect
- Lab 6 Consume data from Kafka using Lambda
[Update 2023-11-06] Initially I planned to deploy Pyflink applications on Amazon Managed Service for Apache Flink, but I changed the plan to use a local Flink cluster deployed on Docker. The main reasons are
- It is not clear how to configure a Pyflink application for the managed service. For example, Apache Flink supports pluggable file systems and the required dependency (eg flink-s3-fs-hadoop-1.15.2.jar) should be placed under the plugins folder. However, the sample Pyflink applications from pyflink-getting-started and amazon-kinesis-data-analytics-blueprints either ignore the S3 jar file for deployment or package it together with other dependencies - none of them uses the S3 jar file as a plugin. I tried multiple different configurations, but all ended up with an error whose code is CodeError.InvalidApplicationCode. I don’t have such an issue when I deploy the app on a local Flink cluster and I haven’t found a way to configure the app for the managed service as yet.
- The Pyflink app for Lab 4 requires the OpenSearch sink connector and the connector is available on 1.16.0+. However, the latest Flink version of the managed service is still 1.15.2 and the sink connector is not available on it. Normally the latest version of the managed service is behind two minor versions of the official release, but it seems to take a little longer to catch up at the moment - the version 1.18.0 was released a while ago.
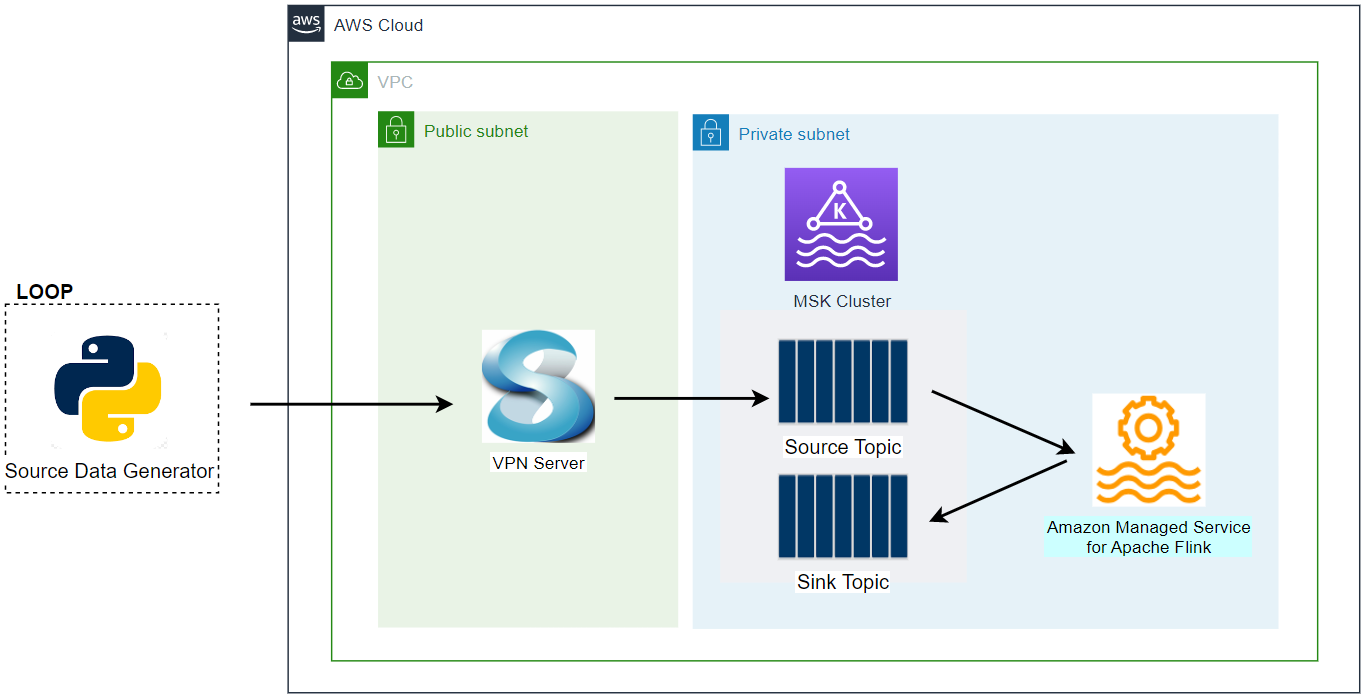
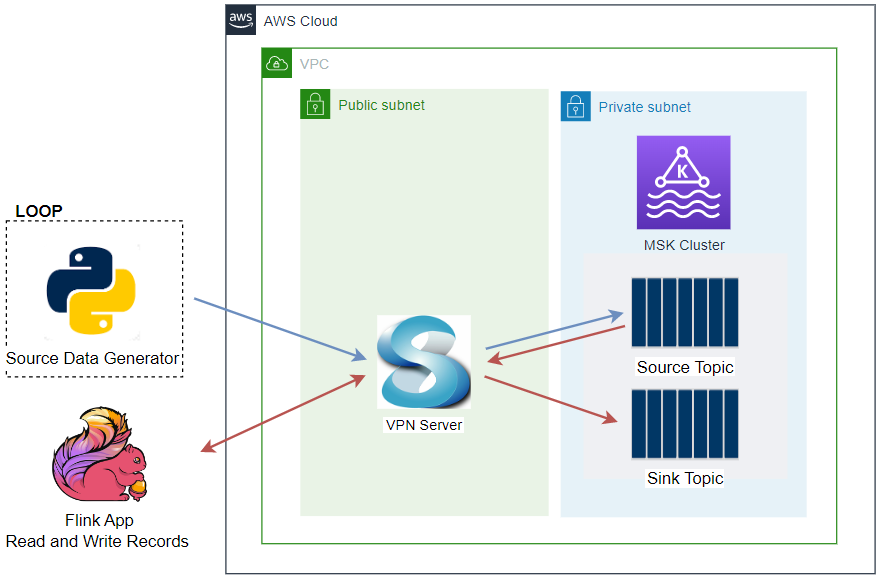
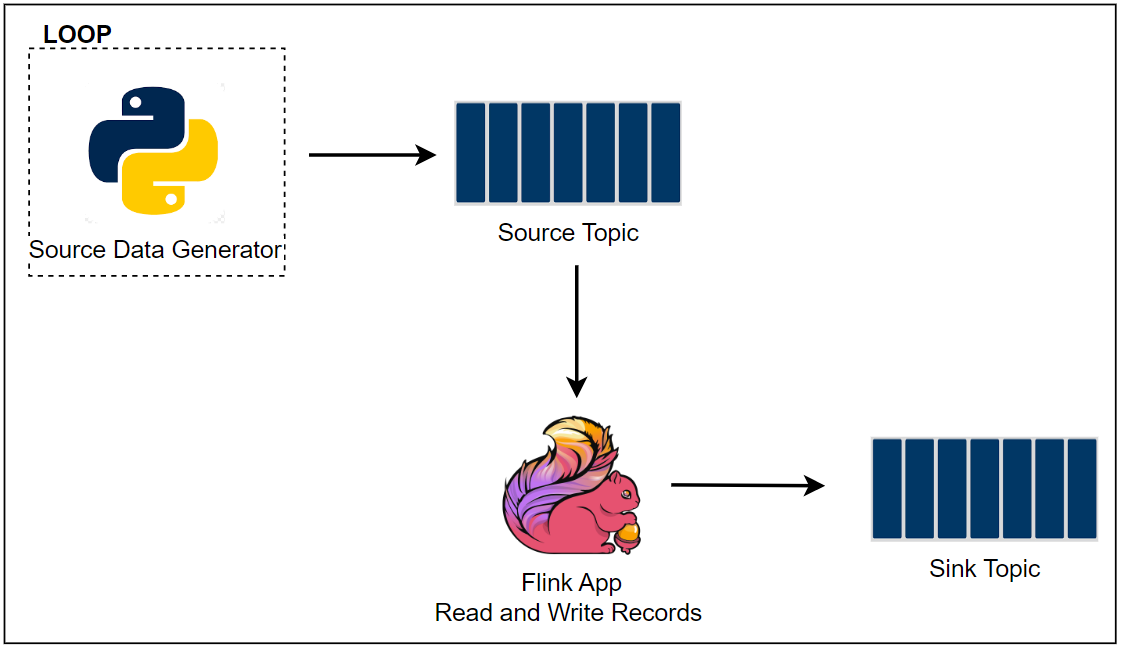
Architecture
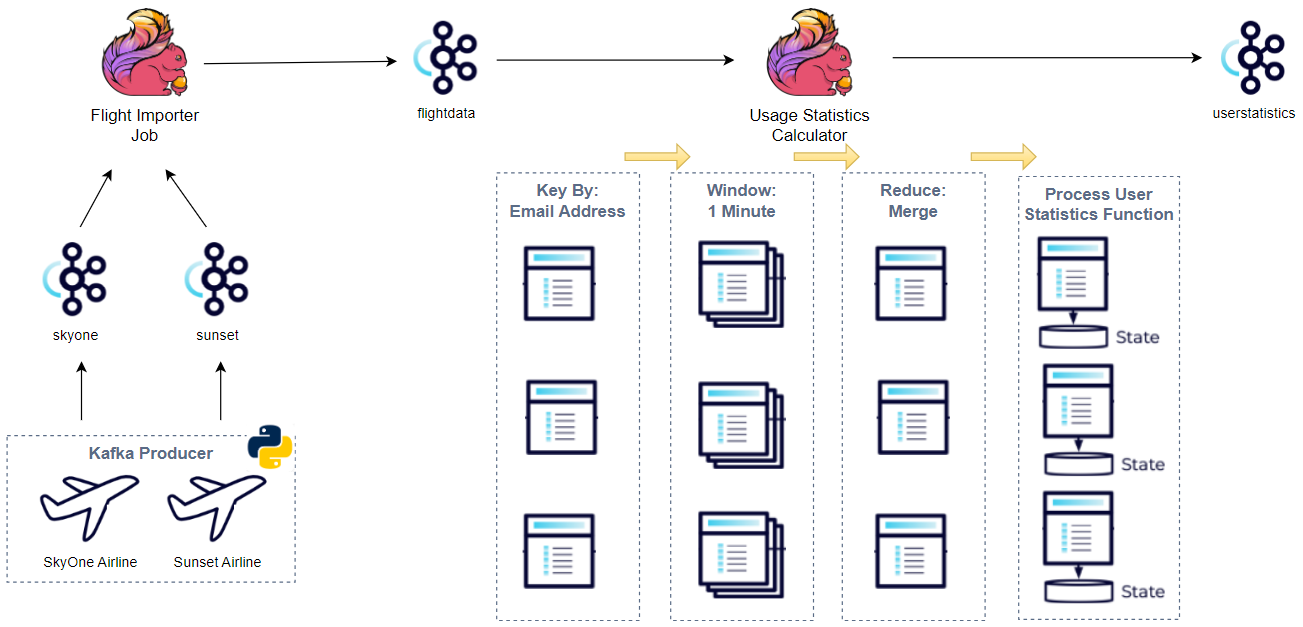
Sample taxi ride data is stored in a S3 bucket, and a Pyflink application reads and ingests it into a Kafka topic on Amazon MSK. As Apache Flink supports both stream and batch processing, we are able to process static data without an issue. We can assume the S3 data is static metadata that needs to be joined into a stream, and this exercise can be useful for data enrichment.
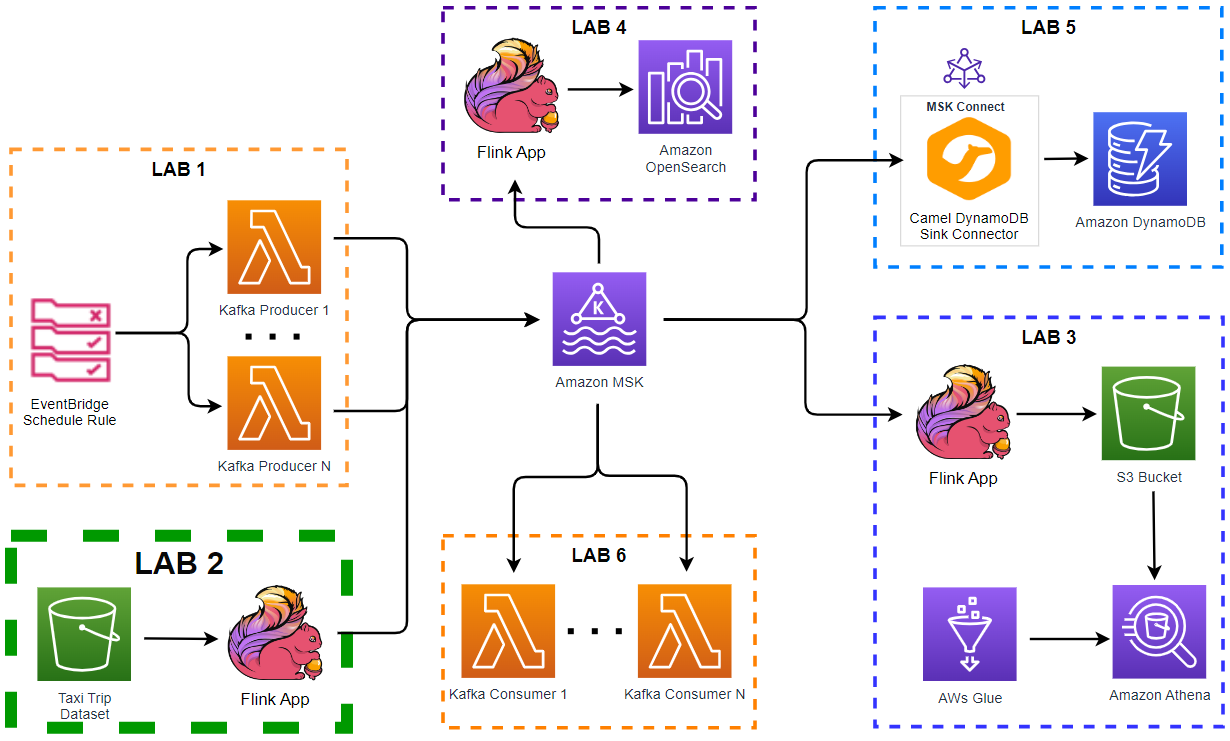
Infrastructure
AWS Infrastructure
The AWS infrastructure is created using Terraform and the source can be found in the GitHub repository of this post - see the previous post for details. The infrastructure can be deployed (as well as destroyed) using Terraform CLI as shown below.
1# initialize
2$ terraform init
3# create an execution plan
4$ terraform plan
5# execute the actions proposed in a Terraform plan
6$ terraform apply -auto-approve=true
7
8# # destroy all remote objects
9# $ terraform destroy -auto-approve=true
Flink Cluster on Docker
Docker Image with Python and Pyflink
The official Flink docker image doesn’t include Python and the Pyflink package, and we need to build a custom image from it. Beginning with placing the S3 jar file (flink-s3-fs-hadoop-1.15.2.jar) under the plugins folder, the following image instals Python and the Pyflink package. It can be built as follows.
1$ docker build -t=real-time-streaming-aws:1.17.1 .
1# Dockerfile
2FROM flink:1.17.1
3
4ARG PYTHON_VERSION
5ENV PYTHON_VERSION=${PYTHON_VERSION:-3.8.10}
6ARG FLINK_VERSION
7ENV FLINK_VERSION=${FLINK_VERSION:-1.17.1}
8
9RUN mkdir ./plugins/s3-fs-hadoop \
10 && cp ./opt/flink-s3-fs-hadoop-${FLINK_VERSION}.jar ./plugins/s3-fs-hadoop
11
12RUN apt-get update -y && \
13 apt-get install -y build-essential libssl-dev zlib1g-dev libbz2-dev libffi-dev liblzma-dev && \
14 wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/${PYTHON_VERSION}/Python-${PYTHON_VERSION}.tgz && \
15 tar -xvf Python-${PYTHON_VERSION}.tgz && \
16 cd Python-${PYTHON_VERSION} && \
17 ./configure --without-tests --enable-shared && \
18 make -j6 && \
19 make install && \
20 ldconfig /usr/local/lib && \
21 cd .. && rm -f Python-${PYTHON_VERSION}.tgz && rm -rf Python-${PYTHON_VERSION} && \
22 ln -s /usr/local/bin/python3 /usr/local/bin/python && \
23 apt-get clean && \
24 rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
25
26# install PyFlink
27RUN pip3 install apache-flink==${FLINK_VERSION}
28
29# add kafka client for Flink SQL client, will be added manually
30RUN wget -P /etc/lib/ https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/org/apache/kafka/kafka-clients/3.2.3/kafka-clients-3.2.3.jar;
Flink Cluster on Docker Compose
The docker compose file includes services for a Flink cluster and Kpow Community Edition. For the Flink cluster, both a single master container (jobmanager) and one task container (taskmanager) are created. The former runs the job Dispatcher and ResourceManager while TaskManager is run in the latter. Once a Flink app (job) is submitted to the Dispatcher, it spawns a JobManager thread and provides the JobGraph for execution. The JobManager requests the necessary processing slots from the ResourceManager and deploys the job for execution once the requested slots have been received.
Kafka bootstrap server addresses and AWS credentials are required for the Flink cluster and kpow app, which are specified as environment variables. The bootstrap server addresses can be obtained via terraform (terraform output -json | jq -r '.msk_bootstrap_brokers_sasl_iam.value') or from AWS Console.
Finally, see the previous post for details about how to configure the kpow app.
1# compose-msk.yml
2# see compose-local-kafka.yml for a local kafka cluster instead of msk
3version: "3.5"
4
5services:
6 jobmanager:
7 image: real-time-streaming-aws:1.17.1
8 command: jobmanager
9 container_name: jobmanager
10 ports:
11 - "8081:8081"
12 networks:
13 - appnet
14 volumes:
15 - ./loader:/etc/flink
16 - ./exporter:/etc/flink/exporter
17 - ./package:/etc/package
18 environment:
19 - BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS=$BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS
20 - RUNTIME_ENV=DOCKER
21 - AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=$AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
22 - AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=$AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
23 # - AWS_SESSION_TOKEN=$AWS_SESSION_TOKEN
24 - |
25 FLINK_PROPERTIES=
26 jobmanager.rpc.address: jobmanager
27 state.backend: filesystem
28 state.checkpoints.dir: file:///tmp/flink-checkpoints
29 heartbeat.interval: 1000
30 heartbeat.timeout: 5000
31 rest.flamegraph.enabled: true
32 web.backpressure.refresh-interval: 10000
33 taskmanager:
34 image: real-time-streaming-aws:1.17.1
35 command: taskmanager
36 container_name: taskmanager
37 networks:
38 - appnet
39 volumes:
40 - flink_data:/tmp/
41 - ./:/etc/flink
42 environment:
43 - BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS=$BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS
44 - RUNTIME_ENV=DOCKER
45 - AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=$AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
46 - AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=$AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
47 # - AWS_SESSION_TOKEN=$AWS_SESSION_TOKEN
48 - |
49 FLINK_PROPERTIES=
50 jobmanager.rpc.address: jobmanager
51 taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots: 5
52 state.backend: filesystem
53 state.checkpoints.dir: file:///tmp/flink-checkpoints
54 heartbeat.interval: 1000
55 heartbeat.timeout: 5000
56 depends_on:
57 - jobmanager
58 kpow:
59 image: factorhouse/kpow-ce:91.5.1
60 container_name: kpow
61 ports:
62 - "3000:3000"
63 networks:
64 - appnet
65 environment:
66 AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: $AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
67 AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: $AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
68 # AWS_SESSION_TOKEN: $AWS_SESSION_TOKEN
69 BOOTSTRAP: $BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS
70 SECURITY_PROTOCOL: SASL_SSL
71 SASL_MECHANISM: AWS_MSK_IAM
72 SASL_JAAS_CONFIG: software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;
73 SASL_CLIENT_CALLBACK_HANDLER_CLASS: software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMClientCallbackHandler
74 env_file: # https://kpow.io/get-started/#individual
75 - ./kpow.env
76
77networks:
78 appnet:
79 name: app-network
80
81volumes:
82 flink_data:
83 driver: local
84 name: flink_data
The Docker Compose services can be deployed as shown below.
1$ docker-compose -f compose-msk.yml up -d
Pyflink Application
Flink Pipeline Jar
We are going to include all dependent Jar files with the --jarfile option, and it only accepts a single Jar file. Therefore, we have to create a custom Uber jar file that consolidates all dependent Jar files. On top of the Apache Kafka SQL Connector, we also need the Amazon MSK Library for AWS Identity and Access Management (MSK IAM Auth) as the MSK cluster is authenticated via IAM. Note that we have to build the Jar file based on the Apache Kafka Connector instead of the Apache Kafka SQL Connector because the MSK IAM Auth library is not compatible with the latter due to shade relocation. After some search, I found an example from the amazon-kinesis-data-analytics-blueprints and was able to modify the POM file with necessary dependencies for this post. The modified POM file can be shown below, and it creates the Uber Jar for this post - lab2-pipeline-1.0.0.jar.
1<!-- package/lab2-pipeline/pom.xml -->
2<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
3 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
4 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
5
6 <groupId>com.amazonaws.services.kinesisanalytics</groupId>
7 <artifactId>lab2-pipeline</artifactId>
8 <version>1.0.0</version>
9 <packaging>jar</packaging>
10
11 <name>Uber Jar for PyFlink App</name>
12
13 <properties>
14 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
15 <flink.version>1.17.1</flink.version>
16 <target.java.version>1.11</target.java.version>
17 <jdk.version>11</jdk.version>
18 <scala.binary.version>2.12</scala.binary.version>
19 <kda.connectors.version>2.0.0</kda.connectors.version>
20 <kda.runtime.version>1.2.0</kda.runtime.version>
21 <kafka.clients.version>2.8.1</kafka.clients.version>
22 <log4j.version>2.17.1</log4j.version>
23 <aws-msk-iam-auth.version>1.1.7</aws-msk-iam-auth.version>
24 </properties>
25
26 <repositories>
27 <repository>
28 <id>apache.snapshots</id>
29 <name>Apache Development Snapshot Repository</name>
30 <url>https://repository.apache.org/content/repositories/snapshots/</url>
31 <releases>
32 <enabled>false</enabled>
33 </releases>
34 <snapshots>
35 <enabled>true</enabled>
36 </snapshots>
37 </repository>
38 </repositories>
39
40 <dependencies>
41
42 <dependency>
43 <groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
44 <artifactId>flink-connector-base</artifactId>
45 <version>${flink.version}</version>
46 </dependency>
47
48 <dependency>
49 <groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
50 <artifactId>flink-connector-kafka</artifactId>
51 <version>${flink.version}</version>
52 </dependency>
53
54 <dependency>
55 <groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
56 <artifactId>flink-connector-files</artifactId>
57 <version>${flink.version}</version>
58 </dependency>
59
60 <dependency>
61 <groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
62 <artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId>
63 <version>${kafka.clients.version}</version>
64 </dependency>
65
66 <dependency>
67 <groupId>software.amazon.msk</groupId>
68 <artifactId>aws-msk-iam-auth</artifactId>
69 <version>${aws-msk-iam-auth.version}</version>
70 </dependency>
71
72 <!-- Add logging framework, to produce console output when running in the IDE. -->
73 <!-- These dependencies are excluded from the application JAR by default. -->
74 <dependency>
75 <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
76 <artifactId>log4j-slf4j-impl</artifactId>
77 <version>${log4j.version}</version>
78 <scope>runtime</scope>
79 </dependency>
80 <dependency>
81 <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
82 <artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId>
83 <version>${log4j.version}</version>
84 <scope>runtime</scope>
85 </dependency>
86 <dependency>
87 <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
88 <artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
89 <version>${log4j.version}</version>
90 <scope>runtime</scope>
91 </dependency>
92 </dependencies>
93
94 <build>
95 <plugins>
96
97 <!-- Java Compiler -->
98 <plugin>
99 <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
100 <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
101 <version>3.8.0</version>
102 <configuration>
103 <source>${jdk.version}</source>
104 <target>${jdk.version}</target>
105 </configuration>
106 </plugin>
107
108 <!-- We use the maven-shade plugin to create a fat jar that contains all necessary dependencies. -->
109 <!-- Change the value of <mainClass>...</mainClass> if your program entry point changes. -->
110 <plugin>
111 <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
112 <artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
113 <version>3.4.1</version>
114 <executions>
115 <!-- Run shade goal on package phase -->
116 <execution>
117 <phase>package</phase>
118 <goals>
119 <goal>shade</goal>
120 </goals>
121 <configuration>
122 <artifactSet>
123 <excludes>
124 <exclude>org.apache.flink:force-shading</exclude>
125 <exclude>com.google.code.findbugs:jsr305</exclude>
126 <exclude>org.slf4j:*</exclude>
127 <exclude>org.apache.logging.log4j:*</exclude>
128 </excludes>
129 </artifactSet>
130 <filters>
131 <filter>
132 <!-- Do not copy the signatures in the META-INF folder.
133 Otherwise, this might cause SecurityExceptions when using the JAR. -->
134 <artifact>*:*</artifact>
135 <excludes>
136 <exclude>META-INF/*.SF</exclude>
137 <exclude>META-INF/*.DSA</exclude>
138 <exclude>META-INF/*.RSA</exclude>
139 </excludes>
140 </filter>
141 </filters>
142 <transformers>
143 <transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.ServicesResourceTransformer"/>
144 </transformers>
145 </configuration>
146 </execution>
147 </executions>
148 </plugin>
149 </plugins>
150
151 <pluginManagement>
152 <plugins>
153
154 <!-- This improves the out-of-the-box experience in Eclipse by resolving some warnings. -->
155 <plugin>
156 <groupId>org.eclipse.m2e</groupId>
157 <artifactId>lifecycle-mapping</artifactId>
158 <version>1.0.0</version>
159 <configuration>
160 <lifecycleMappingMetadata>
161 <pluginExecutions>
162 <pluginExecution>
163 <pluginExecutionFilter>
164 <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
165 <artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
166 <versionRange>[3.1.1,)</versionRange>
167 <goals>
168 <goal>shade</goal>
169 </goals>
170 </pluginExecutionFilter>
171 <action>
172 <ignore/>
173 </action>
174 </pluginExecution>
175 <pluginExecution>
176 <pluginExecutionFilter>
177 <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
178 <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
179 <versionRange>[3.1,)</versionRange>
180 <goals>
181 <goal>testCompile</goal>
182 <goal>compile</goal>
183 </goals>
184 </pluginExecutionFilter>
185 <action>
186 <ignore/>
187 </action>
188 </pluginExecution>
189 </pluginExecutions>
190 </lifecycleMappingMetadata>
191 </configuration>
192 </plugin>
193 </plugins>
194 </pluginManagement>
195 </build>
196</project>
The Uber Jar file can be built using the following script (build.sh).
1# build.sh
2#!/usr/bin/env bash
3SCRIPT_DIR="$(cd $(dirname "$0"); pwd)"
4SRC_PATH=$SCRIPT_DIR/package
5
6# remove contents under $SRC_PATH (except for the folders beginging with lab)
7shopt -s extglob
8rm -rf $SRC_PATH/!(lab*)
9
10## Generate Uber Jar for PyFlink app for MSK cluster with IAM authN
11echo "generate Uber jar for PyFlink app..."
12mkdir $SRC_PATH/lib
13mvn clean install -f $SRC_PATH/lab2-pipeline/pom.xml \
14 && mv $SRC_PATH/lab2-pipeline/target/lab2-pipeline-1.0.0.jar $SRC_PATH/lib \
15 && rm -rf $SRC_PATH/lab2-pipeline/target
Application Source
The Flink application is developed using the Table API. The source uses the FileSystem SQL Connector and a table is created to read records in a S3 bucket. As mentioned earlier, the S3 file system is accessible as the S3 jar file (flink-s3-fs-hadoop-1.17.1.jar) is placed under the plugins folder of the custom Docker image. The sink table is created to write the source records into a Kafka topic. As the Kafka cluster is authenticated via IAM, additional table options are configured.
In the main method, we create all the source and sink tables after mapping relevant application properties. Then the output records are inserted into the output Kafka topic. Note that the output records are printed in the terminal additionally when the app is running locally for ease of checking them.
1# loader/processor.py
2import os
3import re
4import json
5
6from pyflink.table import EnvironmentSettings, TableEnvironment
7
8RUNTIME_ENV = os.environ.get("RUNTIME_ENV", "LOCAL") # LOCAL or DOCKER
9BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS = os.environ.get("BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS") # overwrite app config
10
11env_settings = EnvironmentSettings.in_streaming_mode()
12table_env = TableEnvironment.create(env_settings)
13
14if RUNTIME_ENV == "LOCAL":
15 CURRENT_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
16 PARENT_DIR = os.path.dirname(CURRENT_DIR)
17 PIPELINE_JAR = "lab2-pipeline-1.0.0.jar"
18 APPLICATION_PROPERTIES_FILE_PATH = os.path.join(CURRENT_DIR, "application_properties.json")
19 print(f"file://{os.path.join(PARENT_DIR, 'package', 'lib', PIPELINE_JAR)}")
20 table_env.get_config().set(
21 "pipeline.jars",
22 f"file://{os.path.join(PARENT_DIR, 'package', 'lib', PIPELINE_JAR)}",
23 )
24else:
25 APPLICATION_PROPERTIES_FILE_PATH = "/etc/flink/loader/application_properties.json"
26
27
28def get_application_properties():
29 if os.path.isfile(APPLICATION_PROPERTIES_FILE_PATH):
30 with open(APPLICATION_PROPERTIES_FILE_PATH, "r") as file:
31 contents = file.read()
32 properties = json.loads(contents)
33 return properties
34 else:
35 raise RuntimeError(f"A file at '{APPLICATION_PROPERTIES_FILE_PATH}' was not found")
36
37
38def property_map(props: dict, property_group_id: str):
39 for prop in props:
40 if prop["PropertyGroupId"] == property_group_id:
41 return prop["PropertyMap"]
42
43
44def inject_security_opts(opts: dict, bootstrap_servers: str):
45 if re.search("9098$", bootstrap_servers):
46 opts = {
47 **opts,
48 **{
49 "properties.security.protocol": "SASL_SSL",
50 "properties.sasl.mechanism": "AWS_MSK_IAM",
51 "properties.sasl.jaas.config": "software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;",
52 "properties.sasl.client.callback.handler.class": "software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMClientCallbackHandler",
53 },
54 }
55 return ", ".join({f"'{k}' = '{v}'" for k, v in opts.items()})
56
57
58def create_source_table(table_name: str, file_path: str):
59 stmt = f"""
60 CREATE TABLE {table_name} (
61 id VARCHAR,
62 vendor_id INT,
63 pickup_datetime VARCHAR,
64 dropoff_datetime VARCHAR,
65 passenger_count INT,
66 pickup_longitude VARCHAR,
67 pickup_latitude VARCHAR,
68 dropoff_longitude VARCHAR,
69 dropoff_latitude VARCHAR,
70 store_and_fwd_flag VARCHAR,
71 gc_distance DOUBLE,
72 trip_duration INT,
73 google_distance VARCHAR,
74 google_duration VARCHAR
75 ) WITH (
76 'connector'= 'filesystem',
77 'format' = 'csv',
78 'path' = '{file_path}'
79 )
80 """
81 print(stmt)
82 return stmt
83
84
85def create_sink_table(table_name: str, topic_name: str, bootstrap_servers: str):
86 opts = {
87 "connector": "kafka",
88 "topic": topic_name,
89 "properties.bootstrap.servers": bootstrap_servers,
90 "format": "json",
91 "key.format": "json",
92 "key.fields": "id",
93 "properties.allow.auto.create.topics": "true",
94 }
95
96 stmt = f"""
97 CREATE TABLE {table_name} (
98 id VARCHAR,
99 vendor_id INT,
100 pickup_datetime VARCHAR,
101 dropoff_datetime VARCHAR,
102 passenger_count INT,
103 pickup_longitude VARCHAR,
104 pickup_latitude VARCHAR,
105 dropoff_longitude VARCHAR,
106 dropoff_latitude VARCHAR,
107 store_and_fwd_flag VARCHAR,
108 gc_distance DOUBLE,
109 trip_duration INT,
110 google_distance VARCHAR,
111 google_duration VARCHAR
112 ) WITH (
113 {inject_security_opts(opts, bootstrap_servers)}
114 )
115 """
116 print(stmt)
117 return stmt
118
119
120def create_print_table(table_name: str):
121 stmt = f"""
122 CREATE TABLE sink_print (
123 id VARCHAR,
124 vendor_id INT,
125 pickup_datetime VARCHAR,
126 dropoff_datetime VARCHAR,
127 passenger_count INT,
128 pickup_longitude VARCHAR,
129 pickup_latitude VARCHAR,
130 dropoff_longitude VARCHAR,
131 dropoff_latitude VARCHAR,
132 store_and_fwd_flag VARCHAR,
133 gc_distance DOUBLE,
134 trip_duration INT,
135 google_distance VARCHAR,
136 google_duration VARCHAR
137 ) WITH (
138 'connector'= 'print'
139 )
140 """
141 print(stmt)
142 return stmt
143
144
145def main():
146 #### map source/sink properties
147 props = get_application_properties()
148 ## source
149 source_property_group_key = "source.config.0"
150 source_properties = property_map(props, source_property_group_key)
151 print(">> source properties")
152 print(source_properties)
153 source_table_name = source_properties["table.name"]
154 source_file_path = source_properties["file.path"]
155 ## sink
156 sink_property_group_key = "sink.config.0"
157 sink_properties = property_map(props, sink_property_group_key)
158 print(">> sink properties")
159 print(sink_properties)
160 sink_table_name = sink_properties["table.name"]
161 sink_topic_name = sink_properties["topic.name"]
162 sink_bootstrap_servers = BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS or sink_properties["bootstrap.servers"]
163 ## print
164 print_table_name = "sink_print"
165 #### create tables
166 table_env.execute_sql(create_source_table(source_table_name, source_file_path))
167 table_env.execute_sql(
168 create_sink_table(sink_table_name, sink_topic_name, sink_bootstrap_servers)
169 )
170 table_env.execute_sql(create_print_table(print_table_name))
171 #### insert into sink tables
172 if RUNTIME_ENV == "LOCAL":
173 source_table = table_env.from_path(source_table_name)
174 statement_set = table_env.create_statement_set()
175 statement_set.add_insert(sink_table_name, source_table)
176 statement_set.add_insert(print_table_name, source_table)
177 statement_set.execute().wait()
178 else:
179 table_result = table_env.execute_sql(
180 f"INSERT INTO {sink_table_name} SELECT * FROM {source_table_name}"
181 )
182 print(table_result.get_job_client().get_job_status())
183
184
185if __name__ == "__main__":
186 main()
1// loader/application_properties.json
2[
3 {
4 "PropertyGroupId": "kinesis.analytics.flink.run.options",
5 "PropertyMap": {
6 "python": "processor.py",
7 "jarfile": "package/lib/lab2-pipeline-1.0.0.jar"
8 }
9 },
10 {
11 "PropertyGroupId": "source.config.0",
12 "PropertyMap": {
13 "table.name": "taxi_trip_source",
14 "file.path": "s3://<s3-bucket-name-to-replace>/taxi-csv/"
15 }
16 },
17 {
18 "PropertyGroupId": "sink.config.0",
19 "PropertyMap": {
20 "table.name": "taxi_trip_sink",
21 "topic.name": "taxi-trip",
22 "bootstrap.servers": "localhost:29092"
23 }
24 }
25]
Run Application
Execute on Local Flink Cluster
We can run the application in the Flink cluster on Docker and the steps are shown below. Either the Kafka cluster on Amazon MSK or a local Kafka cluster can be used depending on which Docker Compose file we use. In either way, we can check the job details on the Flink web UI on localhost:8081. Note that, if we use the local Kafka cluster option, we have to start the producer application in a different terminal.
1## prep - update s3 bucket name in loader/application_properties.json
2
3## set aws credentials environment variables
4export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<aws-access-key-id>
5export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<aws-secret-access-key>
6# export AWS_SESSION_TOKEN=<aws-session-token>
7
8## run docker compose service
9# with msk cluster
10docker-compose -f compose-msk.yml up -d
11# # or with local Kafka cluster
12# docker-compose -f compose-local-kafka.yml up -d
13
14## run the producer application in another terminal
15# python producer/app.py
16
17## submit pyflink application
18docker exec jobmanager /opt/flink/bin/flink run \
19 --python /etc/flink/loader/processor.py \
20 --jarfile /etc/flink/package/lib/lab2-pipeline-1.0.0.jar \
21 -d
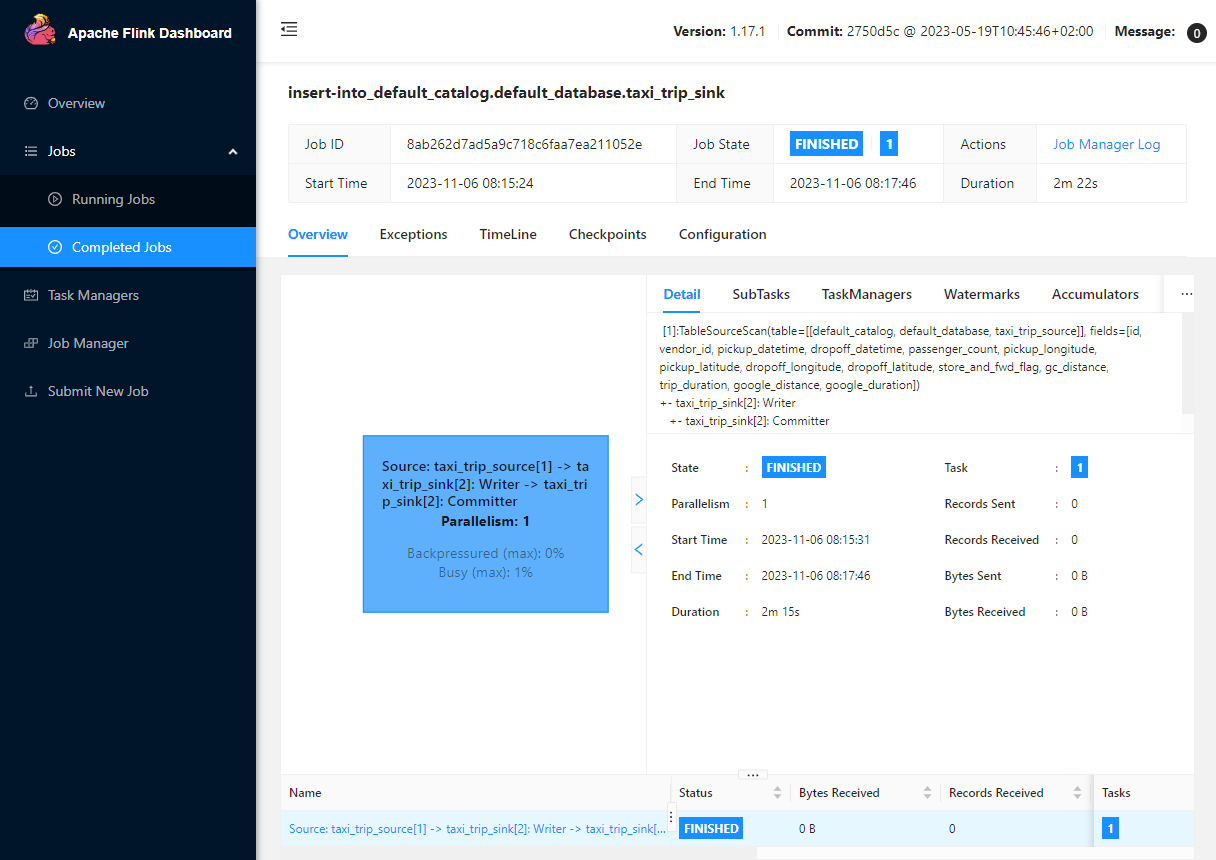
Execute Locally
The application can also be executed locally by specifying the runtime environment (RUNTIME_ENV) and bootstrap server addresses (BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS) as shown below.
1$ RUNTIME_ENV=LOCAL BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS=localhost:29092 python loader/processor.py
Note, in order for the Flink app to be able to access the S3 file system, we have to place the S3 jar file (flink-s3-fs-hadoop-1.17.1.jar) in the lib folder of the Pyflink package. For example, my virtual environment is in the venv folder and I can add the Jar file in the venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/pyflink/lib folder. The package also has the plugins folder but it didn’t work when I placed the Jar file under it.
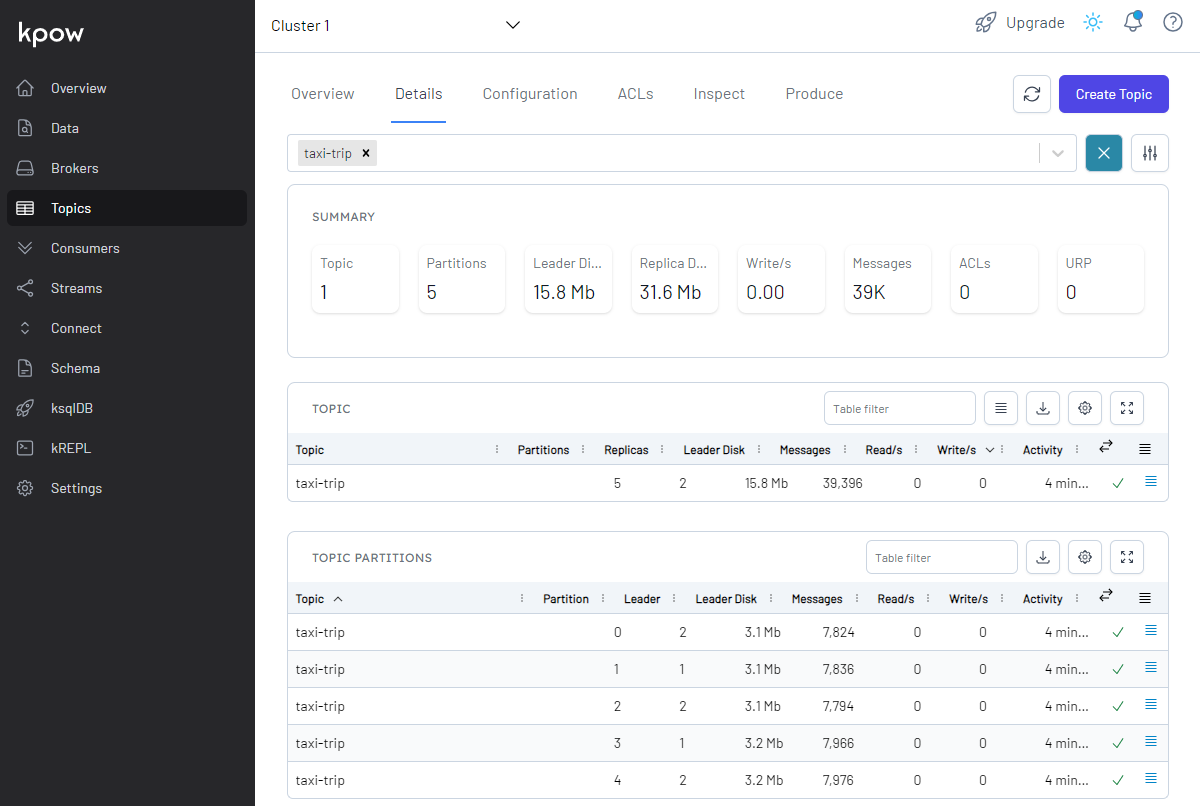
Monitor Topic
We can see the topic (taxi-rides) is created, and the details of the topic can be found on the Topics menu on localhost:3000.
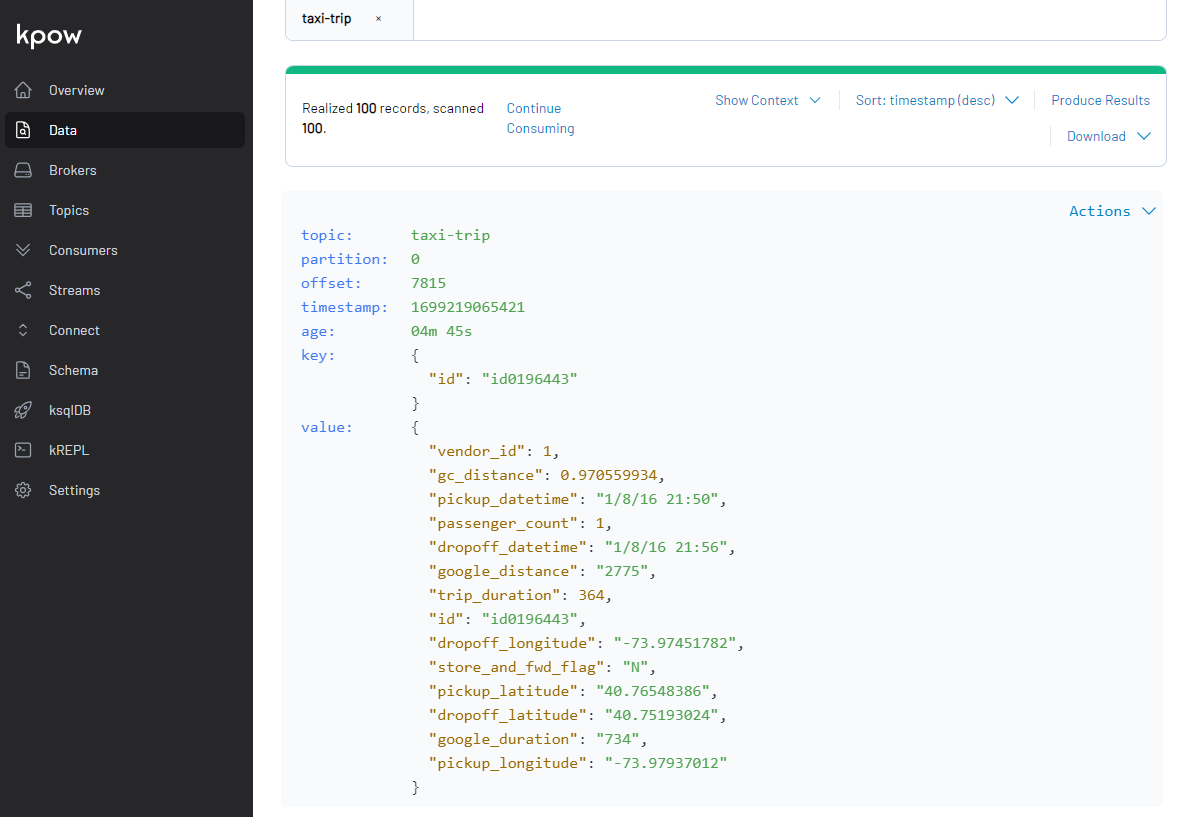
Also, we can inspect topic messages in the Data tab as shown below.
Summary
In this lab, we created a Pyflink application that reads records from S3 and sends them into a Kafka topic. A custom pipeline Jar file was created as the Kafka cluster is authenticated by IAM, and it was demonstrated how to execute the app in a Flink cluster deployed on Docker as well as locally as a typical Python app.

Comments