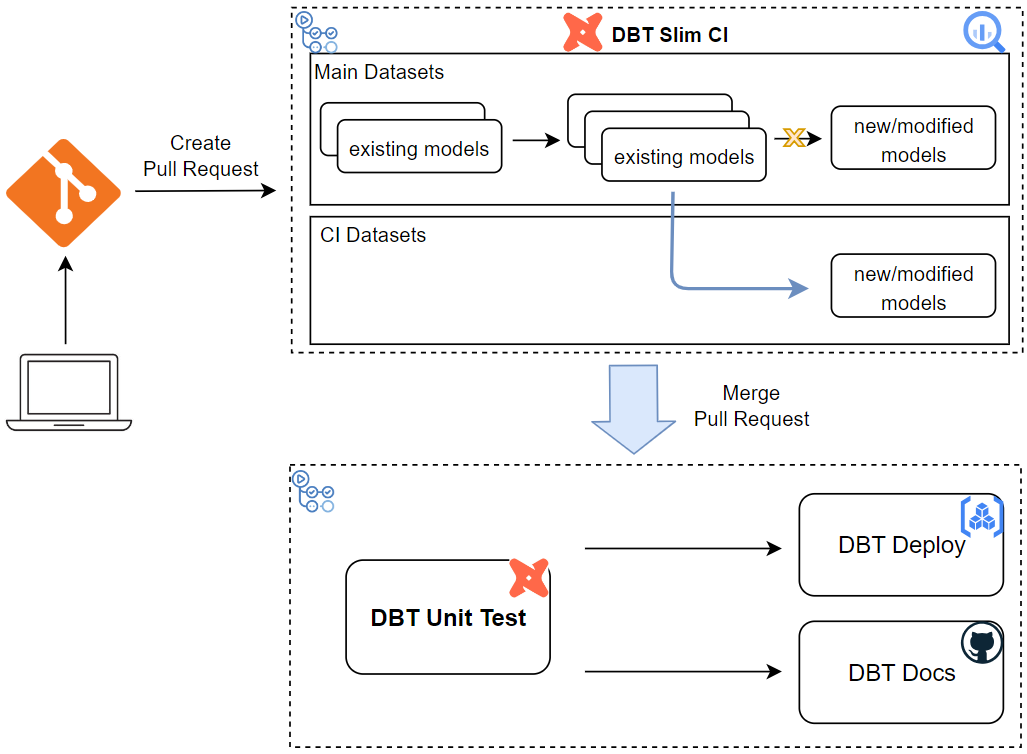
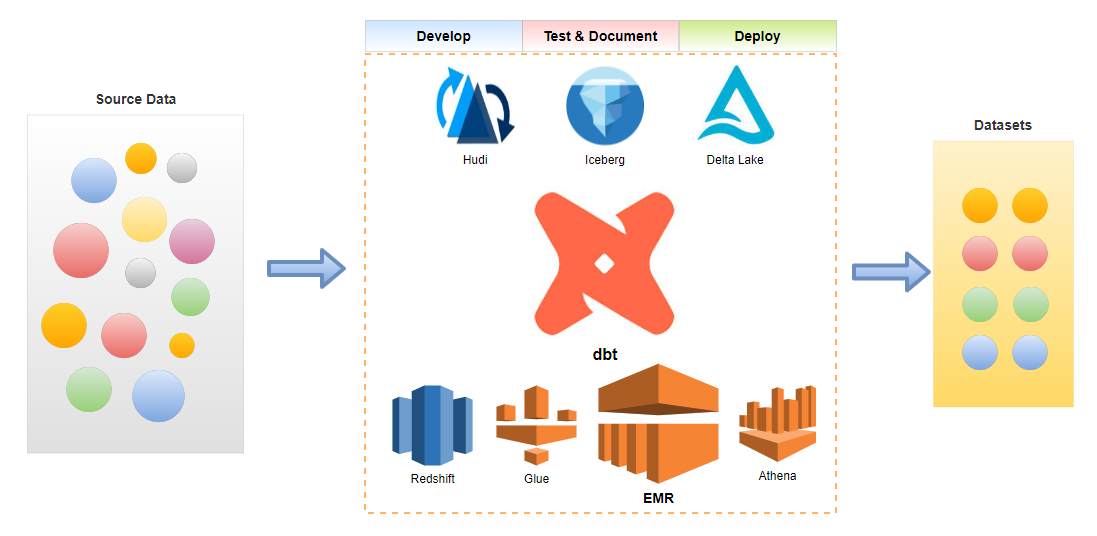
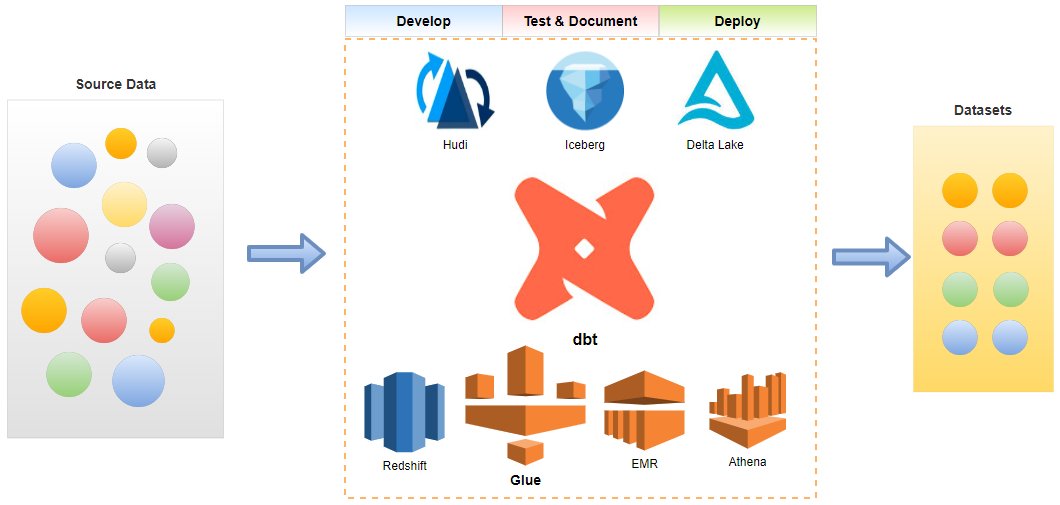
Continuous integration (CI) is the process of ensuring new code integrates with the larger code base, and it puts a great emphasis on testing automation to check that the application is not broken whenever new commits are integrated into the main branch. Continuous delivery (CD) is an extension of continuous integration since it automatically deploys all code changes to a testing and/or production environment after the build stage. CI/CD helps development teams avoid bugs and code failures while maintaining a continuous cycle of software development and updates. In this post, we discuss how to set up a CI/CD pipeline for a data build tool (dbt) project using GitHub Actions where BigQuery is used as the target data warehouse.
The CI/CD process has two workflows - slim-ci and deploy. When a pull request is created to the main branch, the slim-ci workflow is triggered, and it aims to perform tests after building only modified models and its first-order children in a ci dataset. Thanks to the defer feature and state method, it saves time and computational resources for testing a few models in a dbt project. When a pull request is merged to the main branch, the deploy workflow is triggered. It begins with performing unit tests to validate key SQL modelling logic on a small set of static inputs. Once the tests are complete successfully, two jobs are triggered concurrently. The first job builds a Docker container that packages the dbt project and pushes into Artifact Registry while the second one publishes the project documentation into GitHub Pages.
DBT Project
A dbt project is created using fictional pizza shop data. There are three staging data sets (staging_orders, staging_products, and staging_users), and they are loaded as dbt seeds. The project ends up building two SCD Type 2 dimension tables (dim_products and dim_users) and one fact table (fct_orders) - see this post for more details about data modelling of those tables. The structure of the project is listed below, and the source can be found in the GitHub repository of this post.
1pizza_shop
2├── analyses
3├── dbt_project.yml
4├── macros
5├── models
6│ ├── dim
7│ │ ├── dim_products.sql
8│ │ └── dim_users.sql
9│ ├── fct
10│ │ └── fct_orders.sql
11│ ├── schema.yml
12│ ├── sources.yml
13│ ├── src
14│ │ ├── src_orders.sql
15│ │ ├── src_products.sql
16│ │ └── src_users.sql
17│ └── unit_tests.yml
18├── seeds
19│ ├── properties.yml
20│ ├── staging_orders.csv
21│ ├── staging_products.csv
22│ └── staging_users.csv
23├── snapshots
24└── tests
We use two dbt profiles. The dev target is used to manage the dbt models in the main dataset named pizza_shop while the ci target is used by the GitHub Actions Runner. Note that the dataset of the ci target is specified by an environment variable named CI_DATASET, and the value is dynamically determined.
1# dbt_profiles/profiles.yml
2pizza_shop:
3 outputs:
4 dev:
5 type: bigquery
6 method: service-account
7 project: "{{ env_var('GCP_PROJECT_ID') }}"
8 dataset: pizza_shop
9 threads: 4
10 keyfile: "{{ env_var('SA_KEYFILE') }}"
11 job_execution_timeout_seconds: 300
12 job_retries: 1
13 priority: interactive
14 location: australia-southeast1
15 ci:
16 type: bigquery
17 method: service-account
18 project: "{{ env_var('GCP_PROJECT_ID') }}"
19 dataset: "{{ env_var('CI_DATASET') }}"
20 threads: 4
21 keyfile: "{{ env_var('SA_KEYFILE') }}"
22 job_execution_timeout_seconds: 300
23 job_retries: 1
24 priority: interactive
25 location: australia-southeast1
26 target: dev
We first need to load the dbt seed data sets, and it can be achieved using the dbt seed command.
1$ dbt seed --profiles-dir=dbt_profiles --project-dir=pizza_shop --target dev
210:42:18 Running with dbt=1.8.6
310:42:19 Registered adapter: bigquery=1.8.2
410:42:19 Unable to do partial parsing because saved manifest not found. Starting full parse.
510:42:20 [WARNING]: Deprecated functionality
6The `tests` config has been renamed to `data_tests`. Please see
7https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/data-tests#new-data_tests-syntax for more
8information.
910:42:20 Found 6 models, 3 seeds, 4 data tests, 3 sources, 587 macros, 1 unit test
1010:42:20
1110:42:27 Concurrency: 4 threads (target='dev')
1210:42:27
1310:42:27 1 of 3 START seed file pizza_shop.staging_orders ............................... [RUN]
1410:42:27 2 of 3 START seed file pizza_shop.staging_products ............................. [RUN]
1510:42:27 3 of 3 START seed file pizza_shop.staging_users ................................ [RUN]
1610:42:34 2 of 3 OK loaded seed file pizza_shop.staging_products ......................... [INSERT 81 in 6.73s]
1710:42:34 3 of 3 OK loaded seed file pizza_shop.staging_users ............................ [INSERT 10000 in 7.30s]
1810:42:36 1 of 3 OK loaded seed file pizza_shop.staging_orders ........................... [INSERT 20000 in 8.97s]
1910:42:36
2010:42:36 Finished running 3 seeds in 0 hours 0 minutes and 15.34 seconds (15.34s).
2110:42:36
2210:42:36 Completed successfully
2310:42:36
2410:42:36 Done. PASS=3 WARN=0 ERROR=0 SKIP=0 TOTAL=3
Then, we can build the dbt models using the dbt run command. It creates three view models, two table models for the dimension tables, and one incremental model for the fact table.
1$ dbt run --profiles-dir=dbt_profiles --project-dir=pizza_shop --target dev
210:43:18 Running with dbt=1.8.6
310:43:19 Registered adapter: bigquery=1.8.2
410:43:19 Found 6 models, 3 seeds, 4 data tests, 3 sources, 587 macros, 1 unit test
510:43:19
610:43:21 Concurrency: 4 threads (target='dev')
710:43:21
810:43:21 1 of 6 START sql view model pizza_shop.src_orders .............................. [RUN]
910:43:21 2 of 6 START sql view model pizza_shop.src_products ............................ [RUN]
1010:43:21 3 of 6 START sql view model pizza_shop.src_users ............................... [RUN]
1110:43:22 3 of 6 OK created sql view model pizza_shop.src_users .......................... [CREATE VIEW (0 processed) in 1.19s]
1210:43:22 4 of 6 START sql table model pizza_shop.dim_users .............................. [RUN]
1310:43:22 1 of 6 OK created sql view model pizza_shop.src_orders ......................... [CREATE VIEW (0 processed) in 1.35s]
1410:43:22 2 of 6 OK created sql view model pizza_shop.src_products ....................... [CREATE VIEW (0 processed) in 1.35s]
1510:43:22 5 of 6 START sql table model pizza_shop.dim_products ........................... [RUN]
1610:43:25 5 of 6 OK created sql table model pizza_shop.dim_products ...................... [CREATE TABLE (81.0 rows, 13.7 KiB processed) in 2.77s]
1710:43:25 4 of 6 OK created sql table model pizza_shop.dim_users ......................... [CREATE TABLE (10.0k rows, 880.9 KiB processed) in 3.49s]
1810:43:25 6 of 6 START sql incremental model pizza_shop.fct_orders ....................... [RUN]
1910:43:31 6 of 6 OK created sql incremental model pizza_shop.fct_orders .................. [INSERT (20.0k rows, 5.0 MiB processed) in 6.13s]
2010:43:31
2110:43:31 Finished running 3 view models, 2 table models, 1 incremental model in 0 hours 0 minutes and 12.10 seconds (12.10s).
2210:43:31
2310:43:31 Completed successfully
2410:43:31
2510:43:31 Done. PASS=6 WARN=0 ERROR=0 SKIP=0 TOTAL=6
We can check the models are created in the pizza_shop dataset.
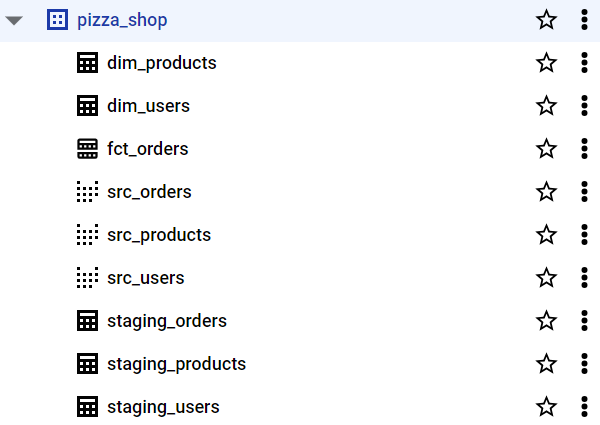
CI/CD Process
The CI/CD process has two workflows - slim-ci and deploy. When a pull request is created to the main branch, the slim-ci workflow is triggered, and it aims to perform tests after building only modified models and its first-order children in a ci dataset. When a pull request is merged to the main branch, the deploy workflow is triggered, and it begins with performing unit tests. Upon successful testing, two jobs are triggered subsequently, which builds/pushes the dbt project in a Docker container and publishes the project documentation.
Prerequisites
Create Repository Variable and Secret
The workflows require a variable that keeps the GCP project ID, and it is accessed by ${{ vars.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}. Also, the service account key is stored as a secret, and it can be retrieved by ${{ secrets.GCP_SA_KEY }}. They can be created on the repository settings.
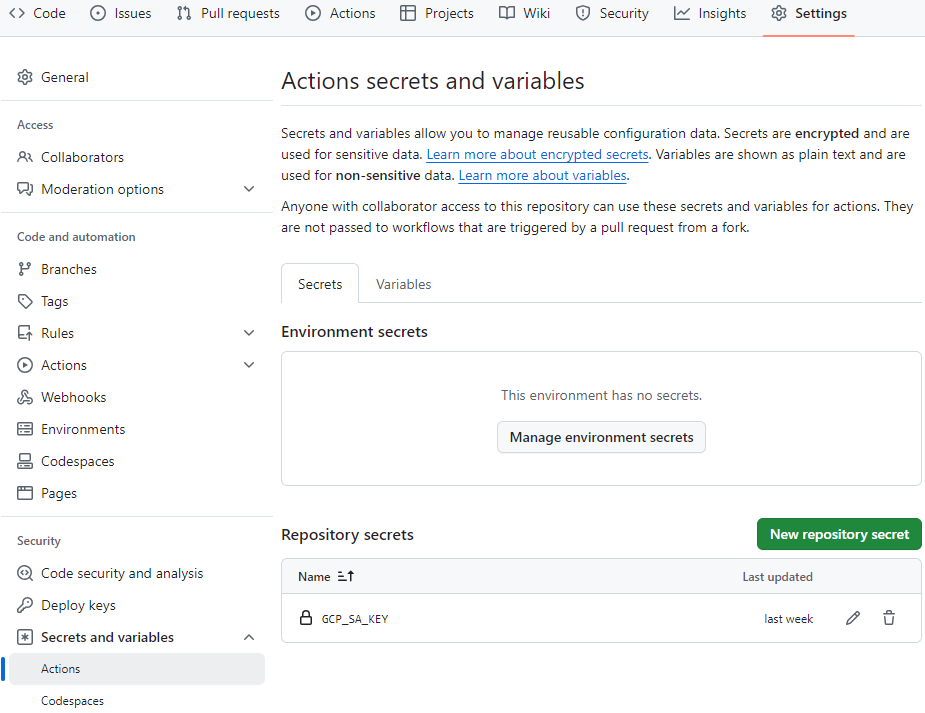
Create GCP Resources and Store DBT Artifact
For the slim-ci, we compare the states between the current and previous invocations, and a manifest from a previous dbt invocation is kept in a GCS bucket. After creating a bucket, we can upload the manifest file from the previous invocation.
1$ gsutil mb gs://dbt-cicd-demo
2
3$ gsutil cp pizza_shop/target/manifest.json gs://dbt-cicd-demo/artifact/manifest.json
4# Copying file://pizza_shop/target/manifest.json [Content-Type=application/json]...
5# - [1 files][608.8 KiB/608.8 KiB]
6# Operation completed over 1 objects/608.8 KiB.
The dbt project is packages in a Docker image and pushed into Artifact Registry repository. The registry for the project can be created as following.
1$ gcloud artifacts repositories create dbt-cicd-demo \
2 --repository-format=docker --location=australia-southeast1
Configure GitHub Pages
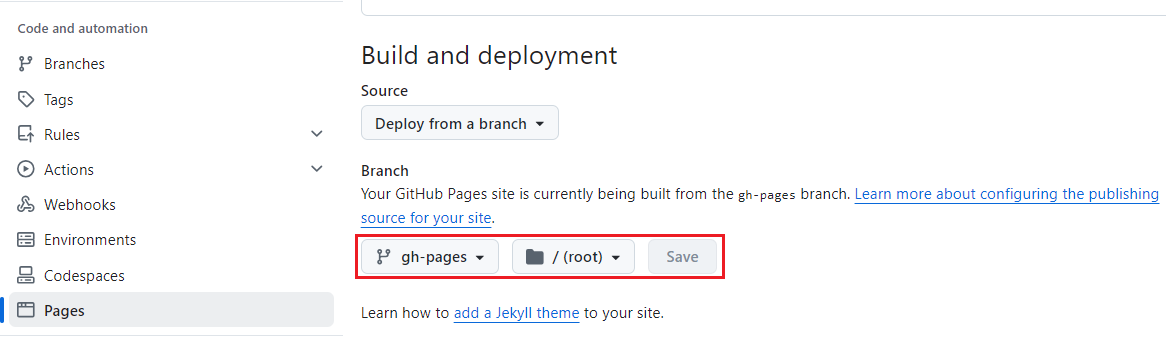
The project documentation is published into GitHub Pages. We first need to enable GitHub Pages on the repository settings. We select the site to be built from the gh-pages branch. To do so, we have to create the dedicated branch and push to the remote repository beforehand.
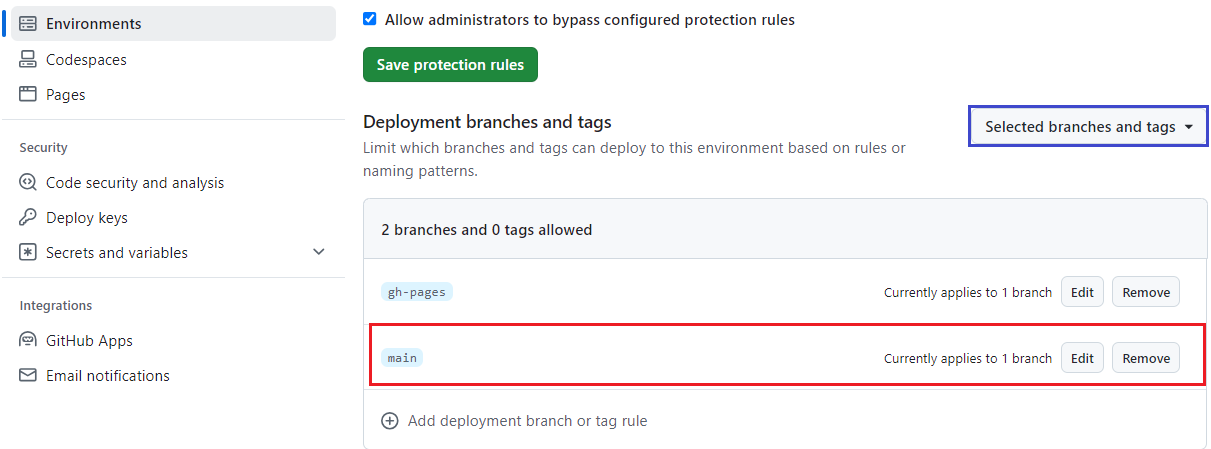
Enabling GitHub Pages creates an environment with protection rules. By default, the site can only be deployed from the gh-pages branch. It can cause the workflow job to fail, and we need to add the main branch in the list. During initial development, we may add one or more feature branches in the list so that the workflow job can be triggered from those branches.
DBT Slim CI
The slim-ci workflow is triggered when a pull request is created to the main branch. It begins with performing prerequisite steps, which covers creating a Python environment, authenticating to GCP, and downloading a dbt manifest file from a GCS bucket. Then, it builds/tests only modified models and its first-order children (--select state:modified+) in a ci dataset without building their upstream parents (--defer). After that, the ci dataset is deleted regardless of whether the build/test step is succeeded or not.
Below shows the main dbt command that is used in the workflow.
1dbt build --profiles-dir=${{ env.DBT_PROFILES_DIR }} --project-dir=pizza_shop --target ci \
2 --select state:modified+ --defer --state ${{github.workspace}}
To show an example outcome, we create a simple change to the fact table by adding a new column before making a pull request,
1-- pizza_shot/models/fct/fct_orders.sql
2...
3SELECT
4 o.order_id,
5 'foo' AS bar -- add new column
6...
Below shows the details of the slim-ci workflow configuration.
1# .github/workflows/slim-ci.yml
2name: slim-ci
3
4on:
5 pull_request:
6 branches: ["main"]
7
8 # Allows you to run this workflow manually from the Actions tab
9 workflow_dispatch:
10
11env:
12 GCP_PROJECT_ID: ${{ vars.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}
13 DBT_PROFILES_DIR: ${{github.workspace}}/dbt_profiles
14 DBT_ARTIFACT_PATH: gs://dbt-cicd-demo/artifact/manifest.json
15
16jobs:
17 dbt-slim-ci:
18 runs-on: ubuntu-latest
19
20 steps:
21 - name: Checkout
22 uses: actions/checkout@v3
23
24 - name: Set up Python
25 uses: actions/setup-python@v1
26 with:
27 python-version: "3.10"
28
29 - name: Create and start virtual environment
30 run: |
31 python -m venv venv
32 source venv/bin/activate
33
34 - name: Install dependencies
35 run: |
36 pip install -r requirements.txt
37
38 - name: Set up service account key file
39 env:
40 GCP_SA_KEY: ${{ secrets.GCP_SA_KEY }}
41 run: |
42 echo ${GCP_SA_KEY} > ${{github.workspace}}/.github/key.json
43 echo SA_KEYFILE=${{github.workspace}}/.github/key.json >> $GITHUB_ENV
44
45 - name: Set up ci dataset
46 run: |
47 echo CI_DATASET=ci_$(date +'%y%m%d_%S')_$(git rev-parse --short "$GITHUB_SHA") >> $GITHUB_ENV
48
49 - name: Authenticate to GCP
50 run: |
51 gcloud auth activate-service-account \
52 dbt-cicd@${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
53 --key-file $SA_KEYFILE --project ${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}
54
55 - name: Download dbt manifest
56 run: gsutil cp ${{ env.DBT_ARTIFACT_PATH }} ${{github.workspace}}
57
58 - name: Install dbt dependencies
59 run: |
60 dbt deps --project-dir=pizza_shop
61
62 - name: Build modified dbt models and its first-order children
63 run: |
64 dbt build --profiles-dir=${{ env.DBT_PROFILES_DIR }} --project-dir=pizza_shop --target ci \
65 --select state:modified+ --defer --state ${{github.workspace}}
66
67 # Hacky way of getting around the bq outputting annoying welcome stuff on first run which breaks jq
68 - name: Check existing CI datasets
69 if: always()
70 shell: bash -l {0}
71 run: bq ls --project_id=${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }} --quiet=true --headless=true --format=json
72
73 - name: Clean up CI datasets
74 if: always()
75 shell: bash -l {0}
76 run: |
77 for dataset in $(bq ls --project_id=${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }} --quiet=true --headless=true --format=json | jq -r '.[].datasetReference.datasetId')
78 do
79 # If the dataset starts with the prefix, delete it
80 if [[ $dataset == $CI_DATASET* ]]; then
81 echo "Deleting $dataset"
82 bq rm -r -f $dataset
83 fi
84 done
In the workflow log, we see only the modified model (fct_orders) is created in a ci dataset - the dataset name is prefixed and suffixed by ci and the commit hash respectively.
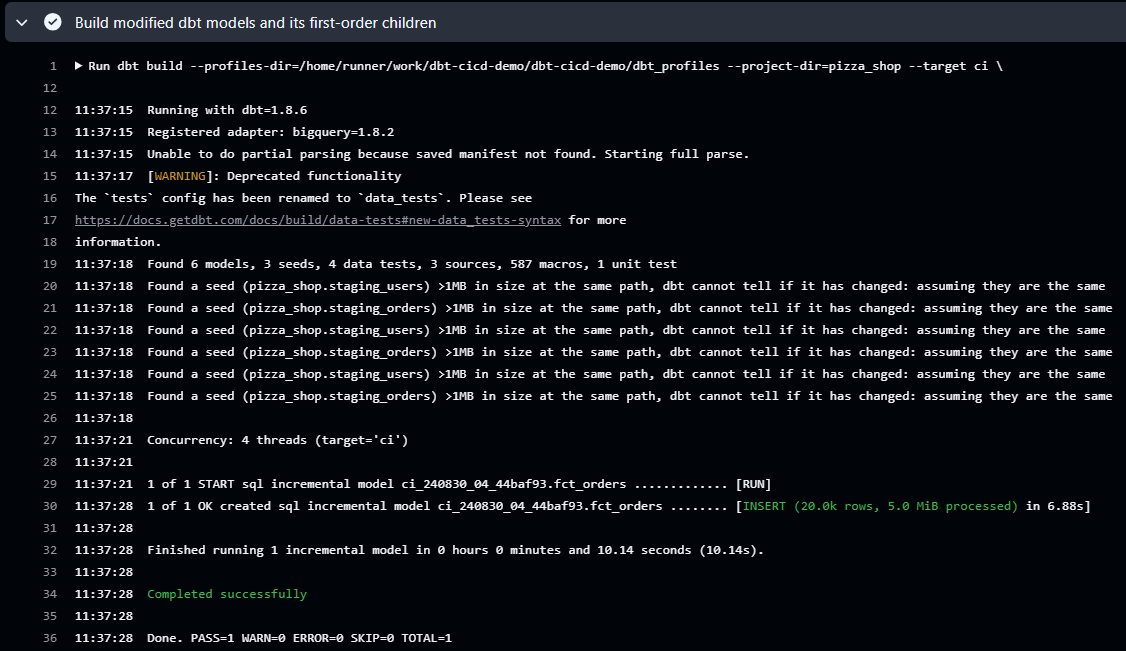
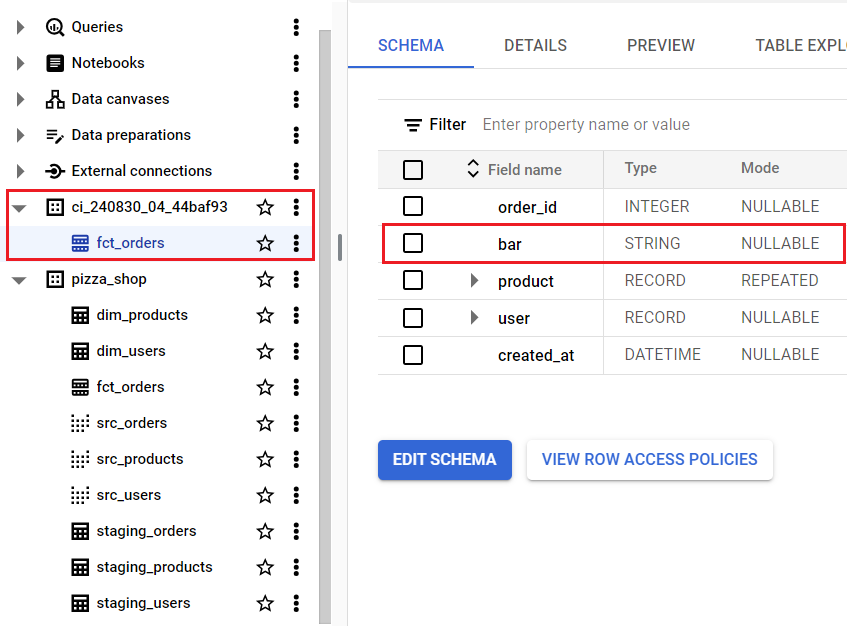
We can see the new column is created in the fct_orders table in the ci dataset.
DBT Deployment
The deploy workflow is triggered when a pull request is merged to the main branch, and it begins with performing unit tests. Upon successful testing, two jobs are triggered subsequently, which builds/pushes the dbt project in a Docker container and publishes the project documentation.
DBT Unit Tests
The dbt-unit-tests job performs unit tests is validating key SQL modelling logic on a small set of static inputs. When developing the users dimension table, we use custom logic to assign values of the valid_from and valid_to columns. We can define a unit testing case of that logic in a YAML file by specifying the name, model, input and expected output.
1-- pizza_shot/models/dim/dim_users.sql
2WITH src_users AS (
3 SELECT * FROM {{ ref('src_users') }}
4)
5SELECT
6 *,
7 created_at AS valid_from,
8 COALESCE(
9 LEAD(created_at, 1) OVER (PARTITION BY user_id ORDER BY created_at),
10 CAST('2199-12-31' AS DATETIME)
11 ) AS valid_to
12FROM src_users
1# pizza_shop/models/unit_tests.yml
2unit_tests:
3 - name: test_is_valid_date_ranges
4 model: dim_users
5 given:
6 - input: ref('src_users')
7 rows:
8 - { created_at: 2024-08-29T10:29:49 }
9 - { created_at: 2024-08-30T10:29:49 }
10 expect:
11 rows:
12 - {
13 created_at: 2024-08-29T10:29:49,
14 valid_from: 2024-08-29T10:29:49,
15 valid_to: 2024-08-30T10:29:49,
16 }
17 - {
18 created_at: 2024-08-30T10:29:49,
19 valid_from: 2024-08-30T10:29:49,
20 valid_to: 2199-12-31T00:00:00,
21 }
Essentially the unit testing job builds the models that have associating unit testing cases (--select +test_type:unit) without populating data (--empty) in a ci dataset. Then, the actual output from the static input is compared with the expected output.
1# build all the models that the unit tests need to run, but empty
2dbt run --profiles-dir=${{ env.DBT_PROFILES_DIR }} --project-dir=pizza_shop --target ci \
3 --select +test_type:unit --empty
4
5# perform the actual unit tests
6dbt test --profiles-dir=${{ env.DBT_PROFILES_DIR }} --project-dir=pizza_shop --target ci \
7 --select test_type:unit
Below shows the details of the dbt-unit-tests job configuration.
1# .github/workflows/deploy.yml
2name: deploy
3
4on:
5 push:
6 branches: ["main"]
7
8 # Allows you to run this workflow manually from the Actions tab
9 workflow_dispatch:
10
11...
12
13env:
14 GCP_LOCATION: australia-southeast1
15 GCP_PROJECT_ID: ${{ vars.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}
16 GCS_TARGET_PATH: gs://dbt-cicd-demo/artifact
17 DBT_PROFILES_DIR: ${{github.workspace}}/dbt_profiles
18
19jobs:
20 dbt-unit-tests:
21 runs-on: ubuntu-latest
22
23 steps:
24 - name: Checkout
25 uses: actions/checkout@v3
26
27 - name: Set up Python
28 uses: actions/setup-python@v1
29 with:
30 python-version: "3.10"
31
32 - name: Create and start virtual environment
33 run: |
34 python -m venv venv
35 source venv/bin/activate
36
37 - name: Install dependencies
38 run: |
39 pip install -r requirements.txt
40
41 - name: Set up service account key file
42 env:
43 GCP_SA_KEY: ${{ secrets.GCP_SA_KEY }}
44 run: |
45 echo ${GCP_SA_KEY} > ${{github.workspace}}/.github/key.json
46 echo SA_KEYFILE=${{github.workspace}}/.github/key.json >> $GITHUB_ENV
47
48 - name: Set up ci dataset
49 run: |
50 echo CI_DATASET=ci_$(date +'%y%m%d_%S')_$(git rev-parse --short "$GITHUB_SHA") >> $GITHUB_ENV
51
52 - name: Authenticate to GCP
53 run: |
54 gcloud auth activate-service-account \
55 dbt-cicd@${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
56 --key-file $SA_KEYFILE --project ${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}
57
58 - name: Install dbt dependencies
59 run: |
60 dbt deps --project-dir=pizza_shop
61
62 - name: Run dbt unit tests
63 run: |
64 # build all the models that the unit tests need to run, but empty
65 dbt run --profiles-dir=${{ env.DBT_PROFILES_DIR }} --project-dir=pizza_shop --target ci \
66 --select +test_type:unit --empty
67 # perform the actual unit tests
68 dbt test --profiles-dir=${{ env.DBT_PROFILES_DIR }} --project-dir=pizza_shop --target ci \
69 --select test_type:unit
70
71 # Hacky way of getting around the bq outputting annoying welcome stuff on first run which breaks jq
72 - name: Check existing CI datasets
73 if: always()
74 shell: bash -l {0}
75 run: bq ls --project_id=${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }} --quiet=true --headless=true --format=json
76
77 - name: Clean up CI datasets
78 if: always()
79 shell: bash -l {0}
80 run: |
81 for dataset in $(bq ls --project_id=${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }} --quiet=true --headless=true --format=json | jq -r '.[].datasetReference.datasetId')
82 do
83 # If the dataset starts with the prefix, delete it
84 if [[ $dataset == $CI_DATASET* ]]; then
85 echo "Deleting $dataset"
86 bq rm -r -f $dataset
87 fi
88 done
In the workflow log, we see it creates two models in a ci dataset and performs unit testing on the users dimension table.
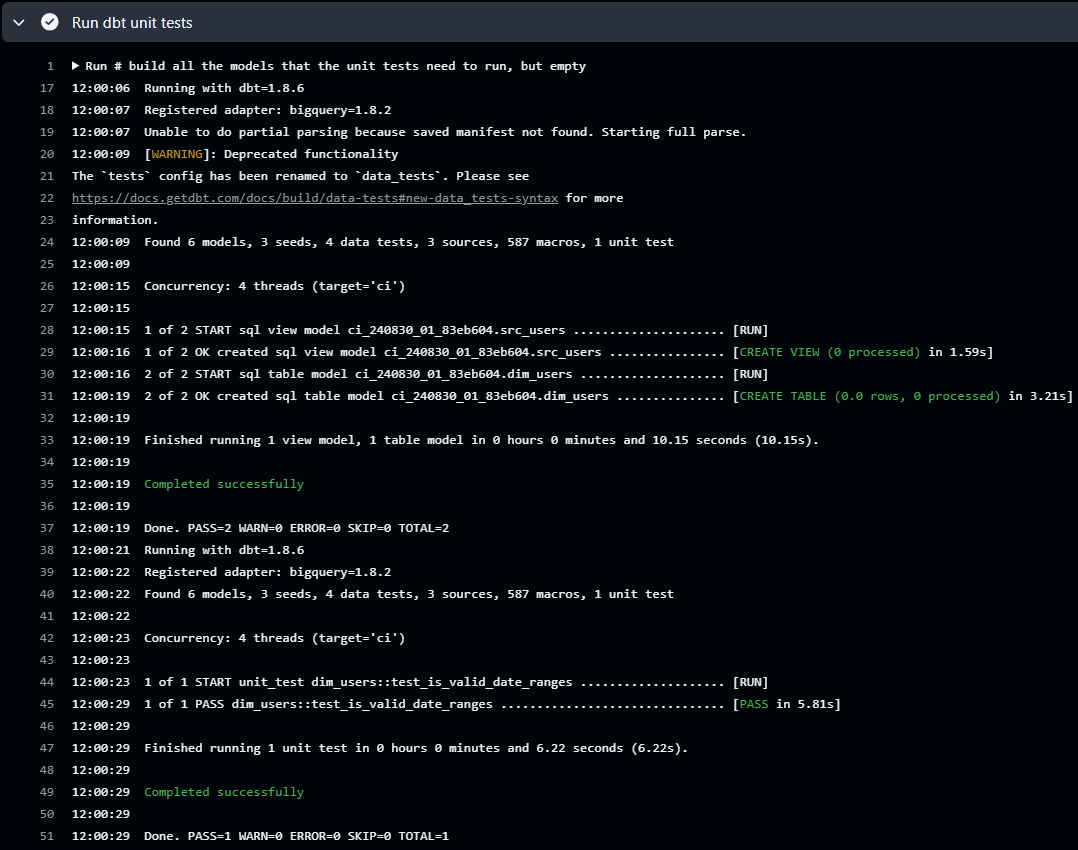
DBT Image Build and Push
The dbt-deploy job packages the dbt project in a Docker container and pushes into an Artifact Registry repository. We use the latest Docker image from dbt labs, installs the Google Cloud CLI, and copies the dbt project and profile files.
1FROM ghcr.io/dbt-labs/dbt-bigquery:1.8.2
2
3ARG GCP_PROJECT_ID
4ARG GCS_TARGET_PATH
5
6ENV GCP_PROJECT_ID=${GCP_PROJECT_ID}
7ENV GCS_TARGET_PATH=${GCS_TARGET_PATH}
8ENV SA_KEYFILE=/usr/app/dbt/key.json
9ENV DBT_ARTIFACT=/usr/app/dbt/pizza_shop/target/manifest.json
10
11## set up gcloud
12RUN apt-get update \
13 && apt-get install -y curl \
14 && curl -sSL https://sdk.cloud.google.com | bash
15
16ENV PATH $PATH:/root/google-cloud-sdk/bin
17COPY key.json key.json
18
19## copy dbt source
20COPY dbt_profiles dbt_profiles
21COPY pizza_shop pizza_shop
22COPY entrypoint.sh entrypoint.sh
23RUN chmod +x entrypoint.sh
24
25RUN dbt deps --project-dir=pizza_shop
26
27ENTRYPOINT ["./entrypoint.sh"]
The entrypoint file runs a dbt command and uploads the resulting dbt manifest file into the GCS bucket. The last step allows the slim-ci workflow to access the latest dbt manifest file for state comparison.
1#!/bin/bash
2set -e
3
4# authenticate to GCP
5gcloud auth activate-service-account \
6 dbt-cicd@$GCP_PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
7 --key-file $SA_KEYFILE --project $GCP_PROJECT_ID
8
9# execute DBT with arguments from container launch
10dbt "$@"
11
12if [ -n "$GCS_TARGET_PATH" ]; then
13 echo "source: $DBT_ARTIFACT, target: $GCS_TARGET_PATH"
14 echo "Copying file..."
15 gsutil --quiet cp $DBT_ARTIFACT $GCS_TARGET_PATH
16fi
We can verify the Docker image by running the dbt test command. As expected, it runs all data tests followed by uploading the dbt manifest file into a GCS bucket.
1# build a docker image
2$ docker build \
3 --build-arg GCP_PROJECT_ID=$GCP_PROJECT_ID \
4 --build-arg GCS_TARGET_PATH=gs://dbt-cicd-demo/artifact \
5 -t dbt:test .
6
7# executes data tests
8$ docker run --rm -it dbt:test \
9 test --profiles-dir=dbt_profiles --project-dir=pizza_shop --target dev
10Activated service account credentials for: [dbt-cicd@GCP_PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com]
1111:53:20 Running with dbt=1.8.3
1211:53:21 Registered adapter: bigquery=1.8.2
1311:53:21 Unable to do partial parsing because saved manifest not found. Starting full parse.
1411:53:22 [WARNING]: Deprecated functionality
15The `tests` config has been renamed to `data_tests`. Please see
16https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/data-tests#new-data_tests-syntax for more
17information.
1811:53:22 Found 6 models, 3 seeds, 4 data tests, 3 sources, 585 macros, 1 unit test
1911:53:22
2011:53:23 Concurrency: 4 threads (target='dev')
2111:53:23
2211:53:23 1 of 5 START test not_null_dim_products_product_key ............................ [RUN]
2311:53:23 2 of 5 START test not_null_dim_users_user_key .................................. [RUN]
2411:53:23 3 of 5 START test unique_dim_products_product_key .............................. [RUN]
2511:53:23 4 of 5 START test unique_dim_users_user_key .................................... [RUN]
2611:53:24 3 of 5 PASS unique_dim_products_product_key .................................... [PASS in 1.44s]
2711:53:24 5 of 5 START unit_test dim_users::test_is_valid_date_ranges .................... [RUN]
2811:53:24 1 of 5 PASS not_null_dim_products_product_key .................................. [PASS in 1.50s]
2911:53:24 4 of 5 PASS unique_dim_users_user_key .......................................... [PASS in 1.54s]
3011:53:25 2 of 5 PASS not_null_dim_users_user_key ........................................ [PASS in 1.59s]
3111:53:28 5 of 5 PASS dim_users::test_is_valid_date_ranges ............................... [PASS in 3.66s]
3211:53:28
3311:53:28 Finished running 4 data tests, 1 unit test in 0 hours 0 minutes and 5.77 seconds (5.77s).
3411:53:28
3511:53:28 Completed successfully
3611:53:28
3711:53:28 Done. PASS=5 WARN=0 ERROR=0 SKIP=0 TOTAL=5
38source: /usr/app/dbt/pizza_shop/target/manifest.json, target: gs://dbt-cicd-demo/artifact
39Copying file...
Below shows the details of the dbt-deploy job configuration.
1# .github/workflows/deploy.yml
2name: deploy
3
4on:
5 push:
6 branches: ["main"]
7
8 # Allows you to run this workflow manually from the Actions tab
9 workflow_dispatch:
10
11...
12
13env:
14 GCP_LOCATION: australia-southeast1
15 GCP_PROJECT_ID: ${{ vars.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}
16 GCS_TARGET_PATH: gs://dbt-cicd-demo/artifact
17 DBT_PROFILES_DIR: ${{github.workspace}}/dbt_profiles
18
19jobs:
20 dbt-unit-tests:
21 ...
22
23 dbt-deploy:
24 runs-on: ubuntu-latest
25
26 needs: dbt-unit-tests
27
28 steps:
29 - name: Checkout
30 uses: actions/checkout@v3
31
32 - name: Set up service account key file
33 env:
34 GCP_SA_KEY: ${{ secrets.GCP_SA_KEY }}
35 run: |
36 echo ${GCP_SA_KEY} > ${{github.workspace}}/.github/key.json
37 echo SA_KEYFILE=${{github.workspace}}/.github/key.json >> $GITHUB_ENV
38
39 - name: Authenticate to GCP
40 run: |
41 gcloud auth activate-service-account \
42 dbt-cicd@${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
43 --key-file $SA_KEYFILE --project ${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}
44
45 - name: Configure docker
46 run: |
47 gcloud auth configure-docker ${{ env.GCP_LOCATION }}-docker.pkg.dev --quiet
48
49 - name: Docker build and push
50 run: |
51 cp ${{github.workspace}}/.github/key.json ${{github.workspace}}/key.json
52 export DOCKER_TAG=${{ env.GCP_LOCATION }}-docker.pkg.dev/${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}/dbt-cicd-demo/dbt:$(git rev-parse --short "$GITHUB_SHA")
53 docker build \
54 --build-arg GCP_PROJECT_ID=${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }} \
55 --build-arg GCS_TARGET_PATH=${{ env.GCS_TARGET_PATH }} \
56 -t ${DOCKER_TAG} ./
57 docker push ${DOCKER_TAG}
DBT Document on GitHub Pages
The dbt-docs job generates the project documentation using the dbt docs generate command, uploads the contents as an artifact and publishes on GitHub Pages. Note that we use the dev target when generating the documentation because it is associated with the main project deployment.
1# .github/workflows/deploy.yml
2name: deploy
3
4on:
5 push:
6 branches: ["main"]
7
8 # Allows you to run this workflow manually from the Actions tab
9 workflow_dispatch:
10
11permissions:
12 contents: read
13 pages: write
14 id-token: write
15
16...
17
18env:
19 GCP_LOCATION: australia-southeast1
20 GCP_PROJECT_ID: ${{ vars.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}
21 GCS_TARGET_PATH: gs://dbt-cicd-demo/artifact
22 DBT_PROFILES_DIR: ${{github.workspace}}/dbt_profiles
23
24jobs:
25 dbt-unit-tests:
26 ...
27
28 dbt-docs:
29 environment:
30 name: github-pages
31 url: ${{ steps.deployment.outputs.page_url }}
32
33 runs-on: ubuntu-latest
34
35 needs: dbt-unit-tests
36
37 steps:
38 - name: Checkout
39 uses: actions/checkout@v3
40
41 - name: Set up Python
42 uses: actions/setup-python@v1
43 with:
44 python-version: "3.10"
45
46 - name: Create and start virtual environment
47 run: |
48 python -m venv venv
49 source venv/bin/activate
50
51 - name: Install dependencies
52 run: |
53 pip install -r requirements.txt
54
55 - name: Set up service account key file
56 env:
57 GCP_SA_KEY: ${{ secrets.GCP_SA_KEY }}
58 run: |
59 echo ${GCP_SA_KEY} > ${{github.workspace}}/.github/key.json
60 echo SA_KEYFILE=${{github.workspace}}/.github/key.json >> $GITHUB_ENV
61
62 - name: Authenticate to GCP
63 run: |
64 gcloud auth activate-service-account \
65 dbt-cicd@${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
66 --key-file $SA_KEYFILE --project ${{ env.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}
67
68 - name: Generate dbt docs
69 id: docs
70 shell: bash -l {0}
71 run: |
72 dbt deps --project-dir=pizza_shop
73 dbt docs generate --profiles-dir=${{ env.DBT_PROFILES_DIR }} --project-dir=pizza_shop \
74 --target dev --target-path dbt-docs
75
76 - name: Upload DBT docs Pages artifact
77 id: build
78 uses: actions/upload-pages-artifact@v2
79 with:
80 path: pizza_shop/dbt-docs
81 name: dbt-docs
82
83 - name: Publish DBT docs to GitHub Pages
84 id: deployment
85 uses: actions/deploy-pages@v2
86 with:
87 artifact_name: dbt-docs
We can check the documentation on this link.

Comments