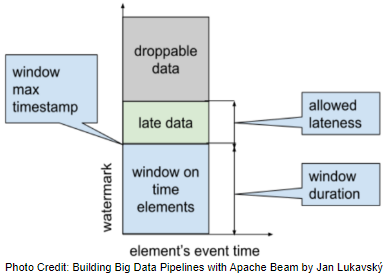
We develop an Apache Beam pipeline that separates droppable elements from the rest of the data. Droppable elements are those that come later when the watermark passes the window max timestamp plus allowed lateness. Using a timer in a Stateful DoFn, droppable data is separated from normal data and dispatched into a side output rather than being discarded silently, which is the default behaviour. Note that this pipeline works in a situation where droppable elements do not appear often, and thus the chance that a droppable element is delivered as the first element in a particular window is low.
- Part 1 Calculate K Most Frequent Words and Max Word Length
- Part 2 Calculate Average Word Length with/without Fixed Look back
- Part 3 Build Sport Activity Tracker with/without SQL
- Part 4 Call RPC Service for Data Augmentation
- Part 5 Call RPC Service in Batch using Stateless DoFn
- Part 6 Call RPC Service in Batch with Defined Batch Size using Stateful DoFn
- Part 7 Separate Droppable Data into Side Output (this post)
- Part 8 Enhance Sport Activity Tracker with Runner Motivation
- Part 9 Develop Batch File Reader and PiSampler using Splittable DoFn
- Part 10 Develop Streaming File Reader using Splittable DoFn
Development Environment
The development environment has an Apache Flink cluster, Apache Kafka cluster and gRPC server. The gRPC server was used in Part 4 to 6. For Flink, we can use either an embedded cluster or a local cluster while Docker Compose is used for the rest. See Part 1 for details about how to set up the development environment. The source of this post can be found in this GitHub repository.
Manage Environment
The Flink and Kafka clusters and gRPC server are managed by the following bash scripts.
./setup/start-flink-env.sh./setup/stop-flink-env.sh
Those scripts accept four flags: -f, -k and -g to start/stop individual resources or -a to manage all of them. We can add multiple flags to start/stop relevant resources. Note that the scripts assume Flink 1.18.1 by default, and we can specify a specific Flink version if it is different from it e.g. FLINK_VERSION=1.17.2 ./setup/start-flink-env.sh.
Below shows how to start resources using the start-up script. We need to launch both the Flink and Kafka clusters if we deploy a Beam pipeline on a local Flink cluster. Otherwise, we can start the Kafka cluster only.
1## start a local flink can kafka cluster
2./setup/start-flink-env.sh -f -k
3# start kafka...
4# [+] Running 6/6
5# ⠿ Network app-network Created 0.0s
6# ⠿ Volume "zookeeper_data" Created 0.0s
7# ⠿ Volume "kafka_0_data" Created 0.0s
8# ⠿ Container zookeeper Started 0.3s
9# ⠿ Container kafka-0 Started 0.5s
10# ⠿ Container kafka-ui Started 0.8s
11# start flink 1.18.1...
12# Starting cluster.
13# Starting standalonesession daemon on host <hostname>.
14# Starting taskexecutor daemon on host <hostname>.
15
16## start a local kafka cluster only
17./setup/start-flink-env.sh -k
18# start kafka...
19# [+] Running 6/6
20# ⠿ Network app-network Created 0.0s
21# ⠿ Volume "zookeeper_data" Created 0.0s
22# ⠿ Volume "kafka_0_data" Created 0.0s
23# ⠿ Container zookeeper Started 0.3s
24# ⠿ Container kafka-0 Started 0.5s
25# ⠿ Container kafka-ui Started 0.8s
Kafka Producer
We create a Kafka producer using the kafka-python package. It generates text messages with the Faker package and sends them to an input topic. Note that we randomly shift back message creation timestamps to simulate late data, and about 20 percent of messages are affected - see below for details about how Beam’s KafkaIO utilises Kafka message timestamp instead of processing timestamp. We can run the producer simply by executing the producer script.
1# utils/faker_shifted_gen.py
2import time
3import argparse
4
5from faker import Faker
6from producer import TextProducer
7
8if __name__ == "__main__":
9 parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(__file__, description="Fake Text Data Generator")
10 parser.add_argument(
11 "--bootstrap_servers",
12 "-b",
13 type=str,
14 default="localhost:29092",
15 help="Comma separated string of Kafka bootstrap addresses",
16 )
17 parser.add_argument(
18 "--topic_name",
19 "-t",
20 type=str,
21 default="input-topic",
22 help="Kafka topic name",
23 )
24 parser.add_argument(
25 "--max_shift_seconds",
26 "-m",
27 type=float,
28 default=15,
29 help="The maximum amount of time that a message create stamp is shifted back.",
30 )
31 parser.add_argument(
32 "--delay_seconds",
33 "-d",
34 type=float,
35 default=1,
36 help="The amount of time that a record should be delayed.",
37 )
38 args = parser.parse_args()
39
40 producer = TextProducer(args.bootstrap_servers, args.topic_name)
41 fake = Faker()
42 Faker.seed(1237)
43
44 while True:
45 text = fake.text(max_nb_chars=10)
46 current = int(time.time())
47 shift = 0
48 if fake.random_int(min=0, max=9) < 2:
49 shift = fake.random_element(range(args.max_shift_seconds))
50 shifted = current - shift
51 producer.send_to_kafka(text=text, timestamp_ms=shifted * 1000)
52 print(
53 f"text - {text}, ts - {current}, shift - {shift} secs - shifted ts {shifted}"
54 )
55 time.sleep(args.delay_seconds)
The producer app sends the input messages using the following Kafka producer class.
1# utils/producer.py
2from kafka import KafkaProducer
3
4
5class TextProducer:
6 def __init__(self, bootstrap_servers: list, topic_name: str) -> None:
7 self.bootstrap_servers = bootstrap_servers
8 self.topic_name = topic_name
9 self.kafka_producer = self.create_producer()
10
11 def create_producer(self):
12 """
13 Returns a KafkaProducer instance
14 """
15 return KafkaProducer(
16 bootstrap_servers=self.bootstrap_servers,
17 value_serializer=lambda v: v.encode("utf-8"),
18 )
19
20 def send_to_kafka(self, text: str, timestamp_ms: int = None):
21 """
22 Sends text to a Kafka topic.
23 """
24 try:
25 args = {"topic": self.topic_name, "value": text}
26 if timestamp_ms is not None:
27 args = {**args, **{"timestamp_ms": timestamp_ms}}
28 self.kafka_producer.send(**args)
29 self.kafka_producer.flush()
30 except Exception as e:
31 raise RuntimeError("fails to send a message") from e
When we run the Kafka producer, it prints messages and associating timestamps. As mentioned, the shifted timestamp values are recorded as message timestamps.
1python utils/faker_shifted_gen.py
2text - Church., ts - 1729476924, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476924
3text - For., ts - 1729476925, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476925
4text - Have., ts - 1729476926, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476926
5text - Health., ts - 1729476927, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476927
6text - Join., ts - 1729476928, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476928
7text - Nice., ts - 1729476929, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476929
8text - New., ts - 1729476930, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476930
9text - Executive., ts - 1729476931, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476931
10text - Memory., ts - 1729476932, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476932
11text - Charge., ts - 1729476933, shift - 11 secs - shifted ts 1729476922
12text - Indeed., ts - 1729476934, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476934
13text - Say then., ts - 1729476935, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476935
14text - Eat nice., ts - 1729476936, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476936
15text - Possible., ts - 1729476937, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476937
16text - Protect., ts - 1729476938, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476938
17text - Shake., ts - 1729476939, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476939
18text - Newspaper., ts - 1729476940, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476940
19text - Language., ts - 1729476941, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476941
20text - Forward., ts - 1729476942, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476942
21text - Order., ts - 1729476943, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476943
22text - Thank., ts - 1729476944, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476944
23text - Growth., ts - 1729476945, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476945
24text - Structure., ts - 1729476946, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476946
25text - Those us., ts - 1729476947, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476947
26text - Decade., ts - 1729476948, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476948
27text - College., ts - 1729476949, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476949
28text - Along., ts - 1729476950, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476950
29text - Sense., ts - 1729476951, shift - 9 secs - shifted ts 1729476942
30text - Land skin., ts - 1729476952, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476952
31text - Service., ts - 1729476953, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476953
32text - While., ts - 1729476954, shift - 10 secs - shifted ts 1729476944
33text - Method., ts - 1729476955, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476955
34text - Spend., ts - 1729476956, shift - 14 secs - shifted ts 1729476942
35text - Drive., ts - 1729476957, shift - 0 secs - shifted ts 1729476957
Beam Pipeline
We develop an Apache Beam pipeline that separates *droppable *elements from the rest of the data. Droppable elements are those that come later when the watermark passes the window max timestamp plus allowed lateness. Using a timer in a Stateful DoFn, droppable data is separated from normal data and dispatched into a side output rather than being discarded silently, which is the default behaviour. Note that this pipeline works in a situation where droppable elements do not appear often, and thus the chance that a droppable element is delivered as the first element in a particular window is low.
Shared Source
We have multiple pipelines that read text messages from an input Kafka topic and write outputs to an output topic. Therefore, the data source and sink transforms are refactored into a utility module as shown below. Note that, the Kafka read and write transforms have an argument called deprecated_read, which forces to use the legacy read when it is set to True. We will use the legacy read in this post to prevent a problem that is described in this GitHub issue. Note further that, by default, timestamp policy of the Kafka read transform is configured to use processing timestamp (wall clock), and it is not possible to simulate late data. We change it to use message creation time (create_time_policy) instead so that both the timestamp of elements and watermark propagation are based on Kafka message (creation) timestamp.
1# chapter3/io_utils.py
2import re
3import typing
4
5import apache_beam as beam
6from apache_beam import pvalue
7from apache_beam.io import kafka
8
9
10def decode_message(kafka_kv: tuple):
11 print(kafka_kv)
12 return kafka_kv[1].decode("utf-8")
13
14
15def tokenize(element: str):
16 return re.findall(r"[A-Za-z\']+", element)
17
18
19class ReadWordsFromKafka(beam.PTransform):
20 def __init__(
21 self,
22 bootstrap_servers: str,
23 topics: typing.List[str],
24 group_id: str,
25 deprecated_read: bool,
26 verbose: bool = False,
27 label: str | None = None,
28 ) -> None:
29 super().__init__(label)
30 self.boostrap_servers = bootstrap_servers
31 self.topics = topics
32 self.group_id = group_id
33 self.verbose = verbose
34 self.expansion_service = None
35 if deprecated_read:
36 self.expansion_service = kafka.default_io_expansion_service(
37 ["--experiments=use_deprecated_read"]
38 )
39
40 def expand(self, input: pvalue.PBegin):
41 return (
42 input
43 | "ReadFromKafka"
44 >> kafka.ReadFromKafka(
45 consumer_config={
46 "bootstrap.servers": self.boostrap_servers,
47 "auto.offset.reset": "latest",
48 # "enable.auto.commit": "true",
49 "group.id": self.group_id,
50 },
51 topics=self.topics,
52 timestamp_policy=kafka.ReadFromKafka.create_time_policy,
53 commit_offset_in_finalize=True,
54 expansion_service=self.expansion_service,
55 )
56 | "DecodeMessage" >> beam.Map(decode_message)
57 | "ExtractWords" >> beam.FlatMap(tokenize)
58 )
59
60
61class WriteOutputsToKafka(beam.PTransform):
62 def __init__(
63 self,
64 bootstrap_servers: str,
65 topic: str,
66 deprecated_read: bool, # TO DO: remove as it applies only to ReadFromKafka
67 label: str | None = None,
68 ) -> None:
69 super().__init__(label)
70 self.boostrap_servers = bootstrap_servers
71 self.topic = topic
72 # TO DO: remove as it applies only to ReadFromKafka
73 self.expansion_service = None
74 if deprecated_read:
75 self.expansion_service = kafka.default_io_expansion_service(
76 ["--experiments=use_deprecated_read"]
77 )
78
79 def expand(self, pcoll: pvalue.PCollection):
80 return pcoll | "WriteToKafka" >> kafka.WriteToKafka(
81 producer_config={"bootstrap.servers": self.boostrap_servers},
82 topic=self.topic,
83 expansion_service=self.expansion_service,
84 )
Pipeline Source
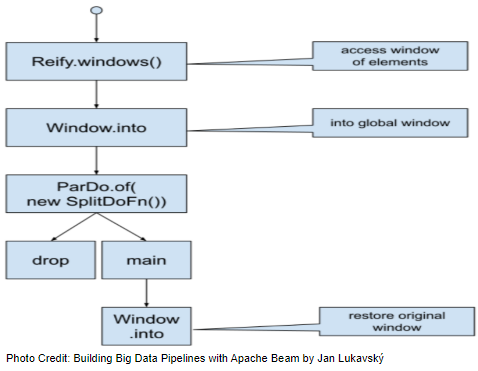
Once messages are read from Kafka and assigned into a fixed window, the main transform (SplitDroppable) is applied to elements, which dispatches (droppable) late data into a side output. Specifically it performs
Reify.Window()- It converts an element in a PCollection into a tuple of element, timestamp, and window.beam.Map(to_kv) | beam.WindowInto(GlobalWindows())- The tuple element is changed into a key-value pair by taking the window as the key, followed by re-windowing the key-value pair into the Global window. Note that we should use the Global window to prevent from (late) elements being discarded silently when the watermark passes the window GC time (or the watermark passes the window max timestamp plus allowed lateness if you like).beam.ParDo(SplitDroppableDataFn(windowing=windowing))- Elements are classified as (droppable) late or normal using the window GC timer and split into the main and side output accordingly.Rewindow(windowing=windowing)- Elements in the main output is re-windowed according to its original window function while those in the droppable output are returned as they are.
Below shows the sequence of transforms of the main transform.
1# chapter3/droppable_data_filter.py
2import os
3import argparse
4import json
5import re
6import typing
7import logging
8
9import apache_beam as beam
10from apache_beam import pvalue, Windowing
11from apache_beam.transforms.trigger import AccumulationMode
12from apache_beam.transforms.timeutil import TimeDomain
13from apache_beam.transforms.userstate import (
14 ReadModifyWriteStateSpec,
15 TimerSpec,
16 on_timer,
17)
18from apache_beam.transforms.window import (
19 GlobalWindows,
20 BoundedWindow,
21 FixedWindows,
22)
23from apache_beam.transforms.util import Reify
24from apache_beam.utils.timestamp import Timestamp
25from apache_beam.options.pipeline_options import PipelineOptions
26from apache_beam.options.pipeline_options import SetupOptions
27
28from io_utils import ReadWordsFromKafka, WriteOutputsToKafka
29
30MAIN_OUTPUT = "main_output"
31DROPPABLE_OUTPUT = "droppable_output"
32
33
34def create_message(
35 element: typing.Union[typing.Tuple[Timestamp, Timestamp, str], str], is_main: bool
36):
37 if is_main:
38 msg = json.dumps(
39 {
40 "start": element[0].seconds(),
41 "end": element[1].seconds(),
42 "word": element[2],
43 }
44 )
45 key = element[2]
46 else:
47 msg = element
48 key = msg
49 logging.info(f"{'main' if is_main else 'droppable'} message - {msg}")
50 return key.encode("utf-8"), msg.encode("utf-8")
51
52
53class SplitDroppable(beam.PTransform):
54 def expand(self, pcoll):
55 windowing: Windowing = pcoll.windowing
56 assert windowing.windowfn != GlobalWindows
57
58 def to_kv(
59 element: typing.Tuple[str, Timestamp, BoundedWindow],
60 ) -> typing.Tuple[str, str]:
61 value, timestamp, window = element
62 return str(window), value
63
64 outputs: pvalue.DoOutputsTuple = (
65 pcoll
66 | Reify.Window()
67 | beam.Map(to_kv)
68 | beam.WindowInto(GlobalWindows())
69 | beam.ParDo(SplitDroppableDataFn(windowing=windowing))
70 .with_outputs(DROPPABLE_OUTPUT, main=MAIN_OUTPUT)
71 .with_input_types(typing.Tuple[str, str])
72 )
73
74 pcolls = {}
75 pcolls[MAIN_OUTPUT] = outputs[MAIN_OUTPUT]
76 pcolls[DROPPABLE_OUTPUT] = outputs[DROPPABLE_OUTPUT]
77
78 return pcolls | Rewindow(windowing=windowing)
79
80
81class SplitDroppableDataFn(beam.DoFn):
82 TOO_LATE = ReadModifyWriteStateSpec("too_late", beam.coders.BooleanCoder())
83 WINDOW_GC_TIMER = TimerSpec("window_gc_timer", TimeDomain.WATERMARK)
84
85 def __init__(self, windowing: Windowing):
86 self.windowing = windowing
87
88 def process(
89 self,
90 element: typing.Tuple[str, str],
91 too_late=beam.DoFn.StateParam(TOO_LATE),
92 window_gc_timer=beam.DoFn.TimerParam(WINDOW_GC_TIMER),
93 ):
94 max_ts = self.get_max_ts(element[0])
95 allowed_lateness_sec = self.windowing.allowed_lateness.micros // 1000000
96 too_late_for_window = too_late.read() or False
97 logging.info(f"string (value) - {element[1]}, window (key) {element[0]}")
98 if too_late_for_window is False:
99 timer_val = max_ts + allowed_lateness_sec
100 logging.info(f"set up eow timer at {timer_val}")
101 window_gc_timer.set(timer_val)
102 if too_late_for_window is True:
103 yield pvalue.TaggedOutput(DROPPABLE_OUTPUT, element[1])
104 else:
105 yield element[1]
106
107 @on_timer(WINDOW_GC_TIMER)
108 def on_window_gc_timer(self, too_late=beam.DoFn.StateParam(TOO_LATE)):
109 too_late.write(True)
110
111 @staticmethod
112 def get_max_ts(window_str: str):
113 """Extract the maximum timestamp of a window string eg) '[0.001, 600.001)'"""
114 bounds = re.findall(r"[\d]+[.\d]+", window_str)
115 assert len(bounds) == 2
116 return float(bounds[1])
117
118
119class Rewindow(beam.PTransform):
120 def __init__(self, label: str | None = None, windowing: Windowing = None):
121 super().__init__(label)
122 self.windowing = windowing
123
124 def expand(self, pcolls):
125 window_fn = self.windowing.windowfn
126 allowed_lateness = self.windowing.allowed_lateness
127 # closing_behavior = self.windowing.closing_behavior # emit always
128 # on_time_behavior = self.windowing.on_time_behavior # fire always
129 timestamp_combiner = self.windowing.timestamp_combiner
130 trigger_fn = self.windowing.triggerfn
131 accumulation_mode = (
132 AccumulationMode.DISCARDING
133 if self.windowing.accumulation_mode == 1
134 else AccumulationMode.ACCUMULATING
135 )
136 main_output = pcolls[MAIN_OUTPUT] | "MainWindowInto" >> beam.WindowInto(
137 windowfn=window_fn,
138 trigger=trigger_fn,
139 accumulation_mode=accumulation_mode,
140 timestamp_combiner=timestamp_combiner,
141 allowed_lateness=allowed_lateness,
142 )
143 return {
144 "main_output": main_output,
145 "droppable_output": pcolls[DROPPABLE_OUTPUT],
146 }
147
148
149class AddWindowTS(beam.DoFn):
150 def process(self, element: str, win_param=beam.DoFn.WindowParam):
151 yield (win_param.start, win_param.end, element)
152
153
154def run(argv=None, save_main_session=True):
155 parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Beam pipeline arguments")
156 parser.add_argument(
157 "--bootstrap_servers",
158 default="host.docker.internal:29092",
159 help="Kafka bootstrap server addresses",
160 )
161 parser.add_argument("--input_topic", default="input-topic", help="Input topic")
162 parser.add_argument("--window_length", default=5, type=int, help="Input topic")
163 parser.add_argument("--allowed_lateness", default=2, type=int, help="Input topic")
164 parser.add_argument(
165 "--output_topic",
166 default=re.sub("_", "-", re.sub(".py$", "", os.path.basename(__file__))),
167 help="Output topic",
168 )
169 parser.add_argument(
170 "--deprecated_read",
171 action="store_true",
172 default="Whether to use a deprecated read. See https://github.com/apache/beam/issues/20979",
173 )
174 parser.set_defaults(deprecated_read=False)
175
176 known_args, pipeline_args = parser.parse_known_args(argv)
177
178 # # We use the save_main_session option because one or more DoFn's in this
179 # # workflow rely on global context (e.g., a module imported at module level).
180 pipeline_options = PipelineOptions(pipeline_args)
181 pipeline_options.view_as(SetupOptions).save_main_session = save_main_session
182 print(f"known args - {known_args}")
183 print(f"pipeline options - {pipeline_options.display_data()}")
184
185 with beam.Pipeline(options=pipeline_options) as p:
186 outputs = (
187 p
188 | "ReadInputsFromKafka"
189 >> ReadWordsFromKafka(
190 bootstrap_servers=known_args.bootstrap_servers,
191 topics=[known_args.input_topic],
192 group_id=f"{known_args.output_topic}-group",
193 deprecated_read=known_args.deprecated_read,
194 )
195 | "Windowing"
196 >> beam.WindowInto(
197 FixedWindows(known_args.window_length),
198 allowed_lateness=known_args.allowed_lateness,
199 accumulation_mode=AccumulationMode.DISCARDING,
200 )
201 | "SpiltDroppable" >> SplitDroppable()
202 )
203
204 (
205 outputs[MAIN_OUTPUT]
206 | "AddWindowTimestamp" >> beam.ParDo(AddWindowTS())
207 | "CreateMainMessage"
208 >> beam.Map(create_message, is_main=True).with_output_types(
209 typing.Tuple[bytes, bytes]
210 )
211 | "WriteToMainTopic"
212 >> WriteOutputsToKafka(
213 bootstrap_servers=known_args.bootstrap_servers,
214 topic="output-normal-topic",
215 deprecated_read=known_args.deprecated_read,
216 )
217 )
218
219 (
220 outputs[DROPPABLE_OUTPUT]
221 | "CreateDroppableMessage"
222 >> beam.Map(create_message, is_main=False).with_output_types(
223 typing.Tuple[bytes, bytes]
224 )
225 | "WriteToDroppableTopic"
226 >> WriteOutputsToKafka(
227 bootstrap_servers=known_args.bootstrap_servers,
228 topic="output-droppable-topic",
229 deprecated_read=known_args.deprecated_read,
230 )
231 )
232
233 logging.getLogger().setLevel(logging.INFO)
234 logging.info("Building pipeline ...")
235
236
237if __name__ == "__main__":
238 run()
Pipeline Test
As described in this documentation, we can test a Beam pipeline as following.
- Create a
TestPipeline. - Create some static, known test input data.
- Create a
PCollectionof input data using theCreatetransform (if bounded source) or aTestStream(if unbounded source) - Apply the transform to the input
PCollectionand save the resulting outputPCollection. - Use
PAssertand its subclasses (or testing utils in Python) to verify that the outputPCollectioncontains the elements that you expect.
There are two test cases. The first case has a pipeline that processes elements as described in the following schedule. Therefore, it is expected to return a single droppable element.
- Watermark propagates to 0
- First element arrives - value: a, timestamp 3 (normal)
- Watermark propagates to 6.999
- Second element arrives - value: b, timestamp 4 (normal)
- Watermark propagates to 7 (Any elements less than 7 will be considered as late!)
- Third element arrives - value: c, timestamp 0 (late)
The second case shows a drawback of the pipeline logic where it treats a late element as normal if it comes as the first element. This is because, when such an element is delivered for the first time, the state is empty and timer is not set up properly. Building Big Data Pipelines with Apache Beam that this example is based on has a solution to fix this issue, and you may check the book if interested.
1# chapter3/droppable_data_filter_test.py
2import unittest
3
4import apache_beam as beam
5from apache_beam.coders import coders
6from apache_beam.transforms.window import IntervalWindow
7from apache_beam.testing.test_pipeline import TestPipeline
8from apache_beam.testing.util import assert_that, equal_to, equal_to_per_window
9from apache_beam.testing.test_stream import TestStream
10from apache_beam.transforms.trigger import AccumulationMode
11from apache_beam.transforms.window import FixedWindows, TimestampedValue
12from apache_beam.options.pipeline_options import PipelineOptions, StandardOptions
13from apache_beam.utils.timestamp import Timestamp
14
15from io_utils import tokenize
16from droppable_data_filter import (
17 SplitDroppable,
18 MAIN_OUTPUT,
19 DROPPABLE_OUTPUT,
20)
21
22
23class DroppableDataFilterTest(unittest.TestCase):
24 def test_windowing_behaviour(self):
25 options = PipelineOptions()
26 options.view_as(StandardOptions).streaming = True
27 now = 0
28 # now = int(time.time())
29 with TestPipeline(options=options) as p:
30 test_stream = (
31 TestStream(coder=coders.StrUtf8Coder())
32 .with_output_types(str)
33 .advance_watermark_to(Timestamp(seconds=now))
34 .add_elements(
35 [TimestampedValue("a", Timestamp(seconds=now + 3))]
36 ) # fine, before watermark - on time
37 .advance_watermark_to(Timestamp(seconds=now + 6.999))
38 .add_elements(
39 [TimestampedValue("b", Timestamp(seconds=now + 4))]
40 ) # late, but within allowed lateness
41 .advance_watermark_to(Timestamp(seconds=now + 7))
42 .add_elements([TimestampedValue("c", now)]) # droppable
43 .advance_watermark_to_infinity()
44 )
45
46 outputs = (
47 p
48 | test_stream
49 | "ExtractWords" >> beam.FlatMap(tokenize)
50 | "Windowing"
51 >> beam.WindowInto(
52 FixedWindows(5),
53 allowed_lateness=2,
54 accumulation_mode=AccumulationMode.DISCARDING,
55 )
56 | "SpiltDroppable" >> SplitDroppable()
57 )
58
59 main_expected = {
60 IntervalWindow(Timestamp(seconds=now), Timestamp(seconds=now + 5)): [
61 "a",
62 "b",
63 ],
64 }
65
66 assert_that(
67 outputs[MAIN_OUTPUT],
68 equal_to_per_window(main_expected),
69 reify_windows=True,
70 label="assert_main",
71 )
72
73 assert_that(
74 outputs[DROPPABLE_OUTPUT], equal_to(["c"]), label="assert_droppable"
75 )
76
77
78class DroppableDataFilterTestFail(unittest.TestCase):
79 @unittest.expectedFailure
80 def test_windowing_behaviour(self):
81 options = PipelineOptions()
82 options.view_as(StandardOptions).streaming = True
83 now = 0
84 # now = int(time.time())
85 with TestPipeline(options=options) as p:
86 test_stream = (
87 TestStream(coder=coders.StrUtf8Coder())
88 .with_output_types(str)
89 .advance_watermark_to(Timestamp(seconds=now + 7.5))
90 .add_elements(
91 [TimestampedValue("c", now)]
92 ) # should be dropped but not!
93 .advance_watermark_to_infinity()
94 )
95
96 outputs = (
97 p
98 | test_stream
99 | "Extract words" >> beam.FlatMap(tokenize)
100 | "Windowing"
101 >> beam.WindowInto(
102 FixedWindows(5),
103 allowed_lateness=2,
104 accumulation_mode=AccumulationMode.DISCARDING,
105 )
106 | "SpiltDroppable" >> SplitDroppable()
107 )
108
109 assert_that(
110 outputs[DROPPABLE_OUTPUT], equal_to(["c"]), label="assert_droppable"
111 )
112
113
114if __name__ == "__main__":
115 unittest.main()
We can execute the pipeline test as shown below.
1python chapter3/droppable_data_filter_test.py
2...
3----------------------------------------------------------------------
4Ran 2 tests in 0.979s
5
6OK (expected failures=1)
Pipeline Execution
Note that the Kafka bootstrap server is accessible on port 29092 outside the Docker network, and it can be accessed on localhost:29092 from the Docker host machine and on host.docker.internal:29092 from a Docker container that is launched with the host network. We use both types of the bootstrap server address - the former is used by the Kafka producer app and the latter by a Java IO expansion service, which is launched in a Docker container. Note further that, for the latter to work, we have to update the /etc/hosts file by adding an entry for host.docker.internal as shown below.
1cat /etc/hosts | grep host.docker.internal
2# 127.0.0.1 host.docker.internal
We need to send messages into the input Kafka topic before executing the pipeline. Input messages can be sent by executing the Kafka text producer - python utils/faker_shifted_gen.py.
When executing the pipeline, we specify only a single known argument that enables to use the legacy read (--deprecated_read) while accepting default values of the other known arguments (bootstrap_servers, input_topic …). The remaining arguments are all pipeline arguments. Note that we deploy the pipeline on a local Flink cluster by specifying the flink master argument (--flink_master=localhost:8081). Alternatively, we can use an embedded Flink cluster if we exclude that argument.
1## start the beam pipeline
2## exclude --flink_master if using an embedded cluster
3python chapter3/droppable_data_filter.py --deprecated_read \
4 --job_name=droppable-data-filter --runner FlinkRunner --flink_master=localhost:8081 \
5 --streaming --environment_type=LOOPBACK --parallelism=3 --checkpointing_interval=10000
On Flink UI, we see the pipeline has two tasks. The first task is until windowing elements in a fixed window while the latter executes the main transform and sends the normal and droppable elements into output topics respectively.
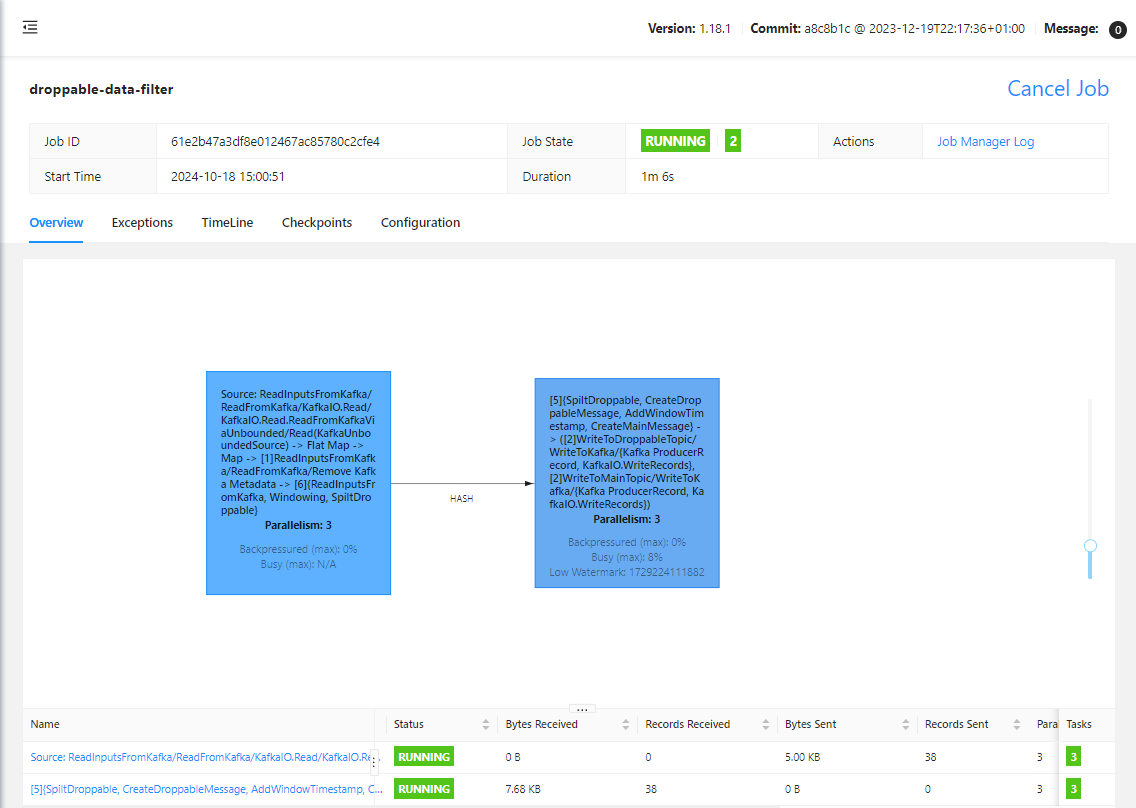
On Kafka UI, we can check messages are sent to the normal and droppable output topics.
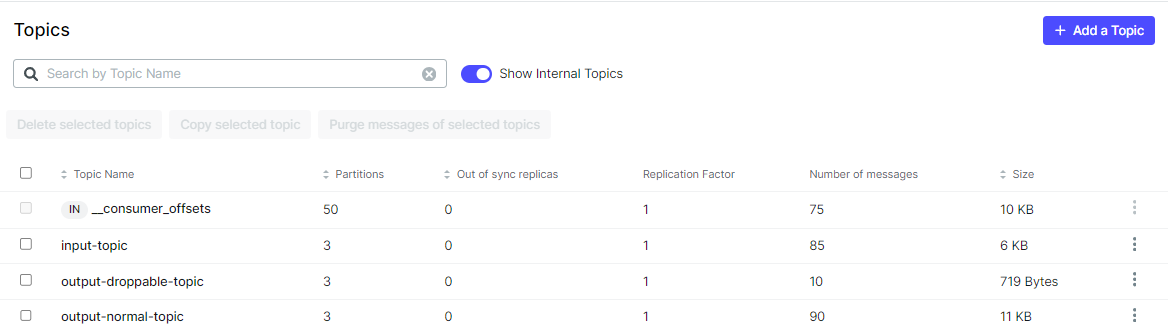




Comments